Page 63 - Read Online
P. 63
Fichera et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2020;4:114-32 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2020.16 Page 121
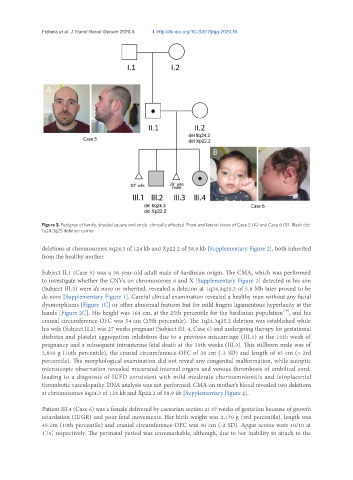
Figure 3. Pedigree of family, shaded square and circle: clinically affected. Front and lateral views of Case 5 (A) and Case 6 (B). Black dot:
1q24.3q25 deletion carrier
deletions at chromosomes 8q24.3 of 124 kb and Xp22.2 of 58.9 kb [Supplementary Figure 2], both inherited
from the healthy mother.
Subject II.1 (Case 5) was a 38-year-old adult male of Sardinian origin. The CMA, which was performed
to investigate whether the CNVs on chromosomes 8 and X [Supplementary Figure 2] detected in his son
(Subject III.2) were de novo or inherited, revealed a deletion at 1q24.3q25.2 of 5.8 Mb later proved to be
de novo [Supplementary Figure 1]. Careful clinical examination revealed a healthy man without any facial
dysmorphisms [Figure 1C] or other abnormal features but for mild fingers ligamentous hyperlaxity at the
[10]
hands [Figure 2C]. His height was 164 cm, at the 25th percentile for the Sardinian population , and his
cranial circumference-OFC was 54 cm (25th percentile). The 1q24.3q25.2 deletion was established while
his wife (Subject II.2) was 27 weeks pregnant (Subject III: 4, Case 6) and undergoing therapy for gestational
diabetes and platelet aggregation inhibitors due to a previous miscarriage (III.1) at the 10th week of
pregnancy and a subsequent intrauterine fetal death at the 39th weeks (III.3). This stillborn male was of
2,850 g (10th percentile), the cranial circumference-OFC of 29 cm (-3 SD) and length of 45 cm (< 3rd
percentile). The morphological examination did not reveal any congenital malformation, while autoptic
microscopic observation revealed macerated internal organs and venous thrombosis of umbilical cord,
leading to a diagnosis of IUFD consistent with mild-moderate chorioamnionitis and fetoplacental
thrombotic vasculopathy. DNA analysis was not performed. CMA on mother’s blood revealed two deletions
at chromosomes 8q24.3 of 124 kb and Xp22.2 of 58.9 kb [Supplementary Figure 2].
Patient III.4 (Case 6) was a female delivered by caesarian section at 37 weeks of gestation because of growth
retardation (IUGR) and poor fetal movements. Her birth weight was 2,170 g (3rd percentile), length was
45 cm (10th percentile) and cranial circumference-OFC was 30 cm (-2 SD). Apgar scores were 10/10 at
1’/5’, respectively. The perinatal period was unremarkable, although, due to her inability to attach to the