Page 60 - Read Online
P. 60
Page 118 Fichera et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2020;4:114-32 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2020.16
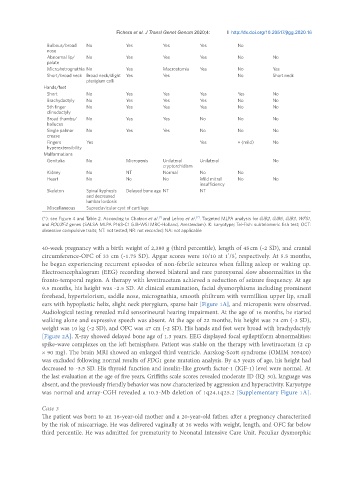
Bulbous/broad No Yes Yes Yes No
nose
Abnormal lip/ No Yes Yes Yes No No
palate
Micro/retrognathia No Yes Macrostomia Yes No Yes
Short/broad neck Broad neck/slight Yes Yes No Short neck
pterigium colli
Hands/feet
Short No Yes Yes Yes Yes No
Brachydactyly No Yes Yes Yes No No
5th finger No Yes Yes Yes No No
clinodactyly
Broad thumbs/ No Yes Yes No No No
halluces
Single palmar No Yes Yes No No No
crease
Fingers Yes Yes + (mild) No
hyperextensibility
Malformations
Genitalia No Micropenis Unilateral Unilateral No
cryptorchidism
Kidney No NT Normal No No
Heart No No No Mild mitral No No
insufficiency
Skeleton Spinal kyphosis Delayed bone age NT NT
and decreased
lumbar lordosis
Miscellaneous Supraclavicular cyst of cartilage
[2]
[1]
(*): see Figure 4 and Table 2. According to Chatron et al. and Lefroy et al. . Targeted MLPA analysis for GJB2, GJB6, GJB3, WFS1,
and POU3F4 genes (SALSA MLPA P163-C1 GJB-WSI MRC-Holland, Amsterdam). K: karyotype; Tel-Fish: subtelomeric fish test; OCT:
obsessive compulsive traits; NT: not tested; NR: not recorded; NA: not applicable
40-week pregnancy with a birth weight of 2,380 g (third percentile), length of 45 cm (-2 SD), and cranial
circumference-OFC of 33 cm (-1.75 SD). Apgar scores were 10/10 at 1’/5’, respectively. At 5.5 months,
he began experiencing recurrent episodes of non-febrile seizures when falling asleep or waking up.
Electroencephalogram (EEG) recording showed bilateral and rare paroxysmal slow abnormalities in the
fronto-temporal region. A therapy with levetiracetam achieved a reduction of seizure frequency. At age
9.5 months, his height was -2.5 SD. At clinical examination, facial dysmorphisms including prominent
forehead, hypertelorism, saddle nose, micrognathia, smooth philtrum with vermillion upper lip, small
ears with hypoplastic helix, slight neck pterygium, sparse hair [Figure 1A], and micropenis were observed.
Audiological testing revealed mild sensorineural hearing impairment. At the age of 16 months, he started
walking alone and expressive speech was absent. At the age of 22 months, his height was 74 cm (-3 SD),
weight was 10 kg (-2 SD), and OFC was 47 cm (-2 SD). His hands and feet were broad with brachydactyly
[Figure 2A]. X-ray showed delayed bone age of 1.3 years. EEG displayed focal epileptiform abnormalities:
spike-wave complexes on the left hemisphere. Patient was stable on the therapy with levetiracetam (2 cp
× 90 mg). The brain MRI showed an enlarged third ventricle. Aarskog-Scott syndrome (OMIM 305400)
was excluded following normal results of FDG1 gene mutation analysis. By 4.5 years of age, his height had
decreased to -3.5 SD. His thyroid function and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) level were normal. At
the last evaluation at the age of five years, Griffiths scale scores revealed moderate ID (IQ: 50), language was
absent, and the previously friendly behavior was now characterized by aggression and hyperactivity. Karyotype
was normal and array-CGH revealed a 10.3-Mb deletion of 1q24.1q25.2 [Supplementary Figure 1A].
Case 3
The patient was born to an 18-year-old mother and a 20-year-old father, after a pregnancy characterized
by the risk of miscarriage. He was delivered vaginally at 36 weeks with weight, length, and OFC far below
third percentile. He was admitted for prematurity to Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Peculiar dysmorphic