Page 145 - Read Online
P. 145
Gropman et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2020;4:429-45 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2020.09 Page 435
1
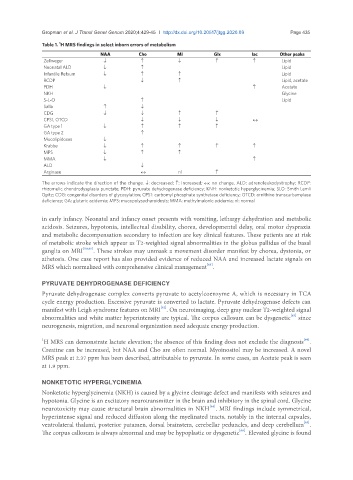
Table 1. H MRS findings in select inborn errors of metabolism
NAA Cho MI Glx lac Other peaks
Zellweger ↓ ↑ ↓ ↑ ↑ Lipid
Neonatal ALD ↓ ↑ Lipid
Infantile Refsum ↓ ↑ ↑ Lipid
RCDP ↓ ↑ Lipid, acetate
PDH ↓ ↑ Acetate
NKH Glycine
S-L-O ↑ Lipid
Salla ↑ ↓
CDG ↓ ↓ ↑ ↑
CPS1, OTCD ↓ ↓ ↓ ↔
GA type 1 ↓ ↑ ↑ ↑
GA type 2 ↑
Mucolipidoses ↓
Krabbe ↓ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑
MPS ↓ ↑ ↑
MMA ↓ ↑
ALD ↓
Arginase ↔ nl ↑
The arrows indicate the direction of the change. ↓: decreased; ↑: increased; ↔: no change. ALD: adrenoleukodystrophy; RCDP:
rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctate; PDH: pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency; KNH: nonketotic hyperglycinemia; SLO: Smith Lemli
Opitz; CDG: congenital disorders of glycosylation; CPS1: carbomyl phosphate synthetase deficiency; OTCD: ornithine transcarbamylase
deficiency; GA: glutaric acidemia; MPS: mucopolysacharoidosis; MMA: methylmalonic acidemia; nl: normal
in early infancy. Neonatal and infancy onset presents with vomiting, lethargy dehydration and metabolic
acidosis. Seizures, hypotonia, intellectual disability, chorea, developmental delay, oral motor dyspraxia
and metabolic decompensation secondary to infection are key clinical features. These patients are at risk
of metabolic stroke which appear as T2-weighted signal abnormalities in the globus pallidus of the basal
ganglia on MRI [59,60] . These strokes may unmask a movement disorder manifest by chorea, dystonia, or
athetosis. One case report has also provided evidence of reduced NAA and increased lactate signals on
[61]
MRS which normalized with comprehensive clinical management .
PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE DEFICIENCY
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex converts pyruvate to acetylcoenzyme A, which is necessary in TCA
cycle energy production. Excessive pyruvate is converted to lactate. Pyruvate dehydrogenase defects can
[62]
manifest with Leigh syndrome features on MRI . On neuroimaging, deep gray nuclear T2-weighted signal
[63]
abnormalities and white matter hyperintensity are typical. The corpus callosum can be dysgenetic since
neurogenesis, migration, and neuronal organization need adequate energy production.
[64]
1 H MRS can demonstrate lactate elevation; the absence of this finding does not exclude the diagnosis .
Creatine can be increased, but NAA and Cho are often normal. Myoinositol may be increased. A novel
MRS peak at 2.37 ppm has been described, attributable to pyruvate. In some cases, an Acetate peak is seen
at 1.9 ppm.
NONKETOTIC HYPERGLYCINEMIA
Nonketotic hyperglycinemia (NKH) is caused by a glycine cleavage defect and manifests with seizures and
hypotonia. Glycine is an excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain and inhibitory in the spinal cord. Glycine
[65]
neurotoxicity may cause structural brain abnormalities in NKH . MRI findings include symmetrical,
hyperintense signal and reduced diffusion along the myelinated tracts, notably in the internal capsules,
[65]
ventrolateral thalami, posterior putamen, dorsal brainstem, cerebellar peduncles, and deep cerebellum .
[66]
The corpus callosum is always abnormal and may be hypoplastic or dysgenetic . Elevated glycine is found