Page 31 - Read Online
P. 31
Przanowski et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2018;2:2 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2017.03 Page 11 of 15
p53 pathway
(P00059)
Wnt signaling pathway
(P00057)
p53 pathway
feedback loop 2
(P04398)
TGF beta
signaling pathway
(P00052)
EGF receptor
signaling pathway
(P00018)
VEGF
signaling pathway
(P00056)
Gonadotropin-releasing
hormone receptor pathway Ras pathway
(P06664) (P04393)
DNA replication
Interleukin (P00017)
signaling pathway
(P00036) CCKR signaling map
Angiogenesis (P06959)
(P00005) Pi3 kinase PDGF signaling
pathway
pathway (P00047)
(P00048)
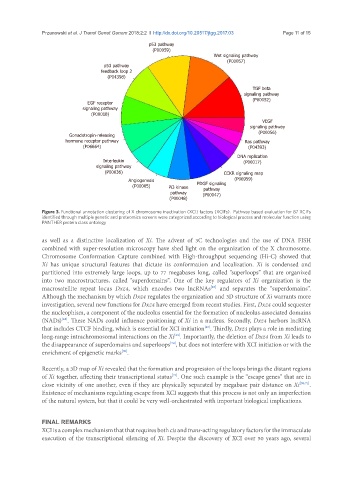
Figure 3. Functional annotation clustering of X chromosome inactivation (XCI) factors (XCIFs). Pathway based evaluation for 87 XCIFs
identified through multiple genetic and proteomics screens were categorized according to biological process and molecular function using
PANTHER protein class ontology
as well as a distinctive localization of Xi. The advent of 3C technologies and the use of DNA FISH
combined with super-resolution microscopy have shed light on the organization of the X chromosome.
Chromosome Conformation Capture combined with High-throughput sequencing (Hi-C) showed that
Xi has unique structural features that dictate its conformation and localization. Xi is condensed and
partitioned into extremely large loops, up to 77 megabases long, called "superloops” that are organized
into two macrostructures, called "superdomains”. One of the key regulators of Xi organization is the
macrosatellite repeat locus Dxz4, which encodes two lncRNAs and separates the “superdomains”.
[67]
Although the mechanism by which Dxz4 regulates the organization and 3D structure of Xi warrants more
investigation, several new functions for Dxz4 have emerged from recent studies. First, Dxz4 could sequester
the nucleophism, a component of the nucleolus essential for the formation of nucleolus-associated domains
(NADs) . These NADs could influence positioning of Xi in a nucleus. Secondly, Dxz4 harbors lncRNA
[68]
that includes CTCF binding, which is essential for XCI initiation . Thirdly, Dxz4 plays a role in mediating
[67]
long-range intrachromosomal interactions on the Xi . Importantly, the deletion of Dxz4 from Xi leads to
[69]
the disappearance of superdomains and superloops , but does not interfere with XCI initiation or with the
[70]
enrichment of epigenetic marks .
[70]
Recently, a 3D map of Xi revealed that the formation and progression of the loops brings the distant regions
of Xi together, affecting their transcriptional status . One such example is the “escape genes” that are in
[71]
close vicinity of one another, even if they are physically separated by megabase pair distance on Xi [70,71] .
Existence of mechanisms regulating escape from XCI suggests that this process is not only an imperfection
of the natural system, but that it could be very well-orchestrated with important biological implications.
FINAL REMARKS
XCI is a complex mechanism that that requires both cis and trans-acting regulatory factors for the immaculate
execution of the transcriptional silencing of Xi. Despite the discovery of XCI over 50 years ago, several