Page 29 - Read Online
P. 29
Przanowski et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2018;2:2 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2017.03 Page 9 of 15
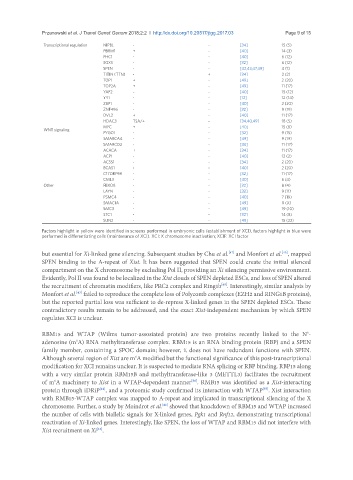
Transcriptional regulation NIPBL - - [34] 15 (5)
PBRM1 + - [40] 14 (3)
PHC1 - - [40] 6 (12)
SOX5 - - [32] 6 (12)
SPEN - - [42,43,47,49] 4 (1)
TITIN (TTN) - + [34] 2 (2)
TOP1 + - [49] 2 (20)
TOP2A + - [49] 11 (17)
YAF2 - - [40] 15 (12)
YY1 - - [12] 12 (14)
ZBP1 - - [40] 2 (20)
ZNF496 - - [32] 9 (19)
DVL2 + - [40] 11 (17)
HDAC3 TSA/+ - [34,40,49] 18 (5)
MYC + - [40] 15 (8)
WNT signaling
PYGO1 - - [32] 9 (15)
SMARCA4 - - [49] 9 (19)
SMARCD2 - - [34] 11 (17)
ACACA + - [34] 11 (17)
ACP1 - - [40] 12 (2)
ACSS1 - - [34] 2 (20)
BCAS1 - - [40] 2 (20)
C17ORF98 - - [32] 11 (17)
CML3 - - [40] 6 (4)
Other FBXO8 - - [32] 8 (4)
LAYN - - [32] 9 (11)
PSMC4 - - [40] 7 (19)
SMAC1A - - [49] X (X)
SMC3 - - [49] 19 (10)
STC1 - - [32] 14 (8)
SUN2 - - [49] 15 (22)
Factors highlight in yellow were identified in screens performed in embryonic cells (establishment of XCI), factors highlight in blue were
performed in differentiating cells (maintenance of XCI). XCI: X chromosome inactivation; XCIF: XCI factor
[47]
but essential for Xi-linked gene silencing. Subsequent studies by Chu et al. and Monfort et al. , mapped
[43]
SPEN binding to the A-repeat of Xist. It has been suggested that SPEN could create the initial silenced
compartment on the X chromosome by excluding Pol II, providing an Xi silencing permissive environment.
Evidently, Pol II was found to be localized in the Xist clouds of SPEN depleted ESCs, and loss of SPEN altered
[49]
the recruitment of chromatin modifiers, like PRC2 complex and Ring1b . Interestingly, similar analysis by
Monfort et al. failed to reproduce the complete loss of Polycomb complexes (EZH2 and RING1B proteins),
[43]
but the reported partial loss was sufficient to de-repress X-linked genes in the SPEN depleted ESCs. These
contradictory results remain to be addressed, and the exact Xist-independent mechanism by which SPEN
regulates XCI is unclear.
RBM15 and WTAP (Wilms tumor-assosiated protein) are two proteins recently linked to the N -
6
adenosine (m A) RNA methyltransferase complex. RBM15 is an RNA binding protein (RBP) and a SPEN
6
family member, containing a SPOC domain; however, it does not have redundant functions with SPEN.
Although several region of Xist are m A modified but the functional significance of this post-transcriptional
6
modification for XCI remains unclear. It is suspected to mediate RNA splicing or RBP binding. RBP15 along
with a very similar protein RBM15B and methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) facilitates the recruitment
[56]
6
of m A machinery to Xist in a WTAP-dependent manner . RMB15 was identified as a Xist-interacting
protein through iDRiP , and a proteomic study confirmed its interaction with WTAP . Xist interaction
[42]
[57]
with RMB15-WTAP complex was mapped to A-repeat and implicated in transcriptional silencing of the X
chromosome. Further, a study by Moindrot et al. showed that knockdown of RBM15 and WTAP increased
[42]
the number of cells with biallelic signals for X-linked genes, Pgk1 and Rnf12, demonstrating transcriptional
reactivation of Xi-linked genes. Interestingly, like SPEN, the loss of WTAP and RBM15 did not interfere with
[42]
Xist recruitment on Xi .