Page 461 - Read Online
P. 461
Maner et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:37 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.60 Page 13 of 40
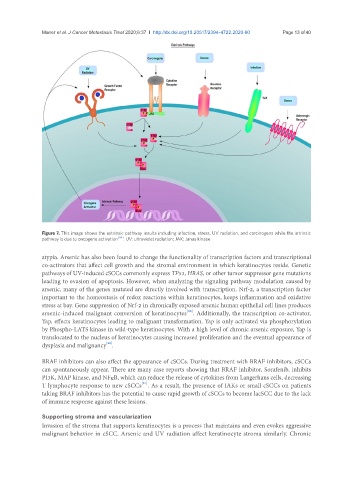
Figure 7. This image shows the extrinsic pathway insults including infection, stress, UV radiation, and carcinogens while the intrinsic
pathway is due to oncogene activation [86] . UV: ultraviolet radiation; JAK: Janus kinase
atypia. Arsenic has also been found to change the functionality of transcription factors and transcriptional
co-activators that affect cell growth and the stromal environment in which keratinocytes reside. Genetic
pathways of UV-induced cSCCs commonly express TP53, HRAS, or other tumor suppressor gene mutations
leading to evasion of apoptosis. However, when analyzing the signaling pathway modulation caused by
arsenic, many of the genes mutated are directly involved with transcription. Nrf-2, a transcription factor
important to the homeostasis of redox reactions within keratinocytes, keeps inflammation and oxidative
stress at bay. Gene suppression of Nrf-2 in chronically exposed arsenic human epithelial cell lines produces
[88]
arsenic-induced malignant conversion of keratinocytes . Additionally, the transcription co-activator,
Yap, effects keratinocytes leading to malignant transformation. Yap is only activated via phosphorylation
by Phospho-LATS kinase in wild-type keratinocytes. With a high level of chronic arsenic exposure, Yap is
translocated to the nucleus of keratinocytes causing increased proliferation and the eventual appearance of
[90]
dysplasia and malignancy .
BRAF inhibitors can also affect the appearance of cSCCs. During treatment with BRAF inhibitors, cSCCs
can spontaneously appear. There are many case reports showing that BRAF inhibitor, Sorafenib, inhibits
PI3K, MAP kinase, and NFκB, which can reduce the release of cytokines from Langerhans cells, decreasing
[91]
T lymphocyte response to new cSCCs . As a result, the presence of IAKs or small cSCCs on patients
taking BRAF inhibitors has the potential to cause rapid growth of cSCCs to become lacSCC due to the lack
of immune response against these lesions.
Supporting stroma and vascularization
Invasion of the stroma that supports keratinocytes is a process that maintains and even evokes aggressive
malignant behavior in cSCC. Arsenic and UV radiation affect keratinocyte stroma similarly. Chronic