Page 113 - Read Online
P. 113
Page 8 of 12 Schofield et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:10 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.43
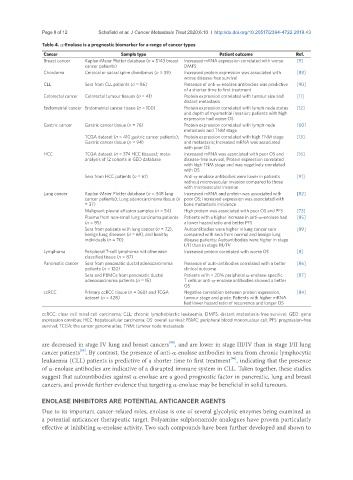
Table 4. a-Enolase is a prognostic biomarker for a range of cancer types
Cancer Sample type Patient outcome Ref.
Breast cancer Kaplan-Meier Plotter database (n = 5143 breast Increased mRNA expression correlated with worse [9]
cancer patients) DMFS
Chordoma Cervical or sacral spine chordomas (n = 39) Increased protein expression was associated with [83]
worse disease-free survival
CLL Sera from CLL patients (n = 86) Presence of anti-a-enolase antibodies was predictive [90]
of a shorter time to first treatment
Colorectal cancer Colorectal tumour tissues (n = 41) Protein expression correlated with tumour size and [11]
distant metastasis
Endometrial cancer Endometrial cancer tissue (n = 100) Protein expression correlated with lymph node status [12]
and depth of myometrial invasion; patients with high
expression had worse OS
Gastric cancer Gastric cancer tissue (n = 76) Protein expression correlated with lymph node [60]
metastasis and TNM stage
TCGA dataset (n = 410 gastric cancer patients); Protein expression correlated with high TNM stage [13]
Gastric cancer tissue (n = 94) and metastasis; Increased mRNA was associated
with poor OS
HCC TCGA dataset (n = 374 HCC tissues); meta- Increased mRNA was associated with poor OS and [16]
analysis of 12 cohorts in GEO database disease-free survival; Protein expression correlated
with high TNM stage and was negatively correlated
with OS
Sera from HCC patients (n = 61) Anti-a-enolase antibodies were lower in patients [91]
without microvascular invasion compared to those
with microvascular invasion
Lung cancer Kaplan-Meier Plotter database (n = 348 lung Increased mRNA and protein was associated with [82]
cancer patients); Lung adenocarcinoma tissue (n poor OS; Increased expression was associated with
= 37) bone metastasis incidence
Malignant pleural effusion samples (n = 54) High protein was associated with poor OS and PFS [73]
Plasma from non-small lung carcinoma patients Patients with a higher increase in anti-a-enolase had [85]
(n = 85) a lower hazard ratio and better PFS
Sera from patients with lung cancer (n = 72), Autoantibodies were higher in lung cancer sera [89]
benign lung diseases (n = 69), and healthy compared with sera from normal and benign lung
individuals (n = 70) disease patients; Autoantibodies were higher in stage
I/II than in stage III/IV
Lymphoma Peripheral T-cell lymphoma not otherwise Increased protein correlated with worse OS [8]
classified tissue (n = 87)
Pancreatic cancer Sera from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma Presence of auto-antibodies correlated with a better [86]
patients (n = 120) clinical outcome
Sera and PBMCs from pancreatic ductal Patients with > 20% peripheral a-enolase-specific [87]
adenocarcinoma patients (n = 15) T cells or anti-a-enolase antibodies showed a better
OS
ccRCC Primary ccRCC tissue (n = 360) and TCGA Negative correlation between protein expression, [84]
dataset (n = 428) tumour stage and grade. Patients with higher mRNA
had lower hazard ratio of recurrence and longer OS
ccRCC: clear cell renal cell carcinoma; CLL: chronic lymphoblastic leukaemia; DMFS: distant metastasis-free survival; GEO: gene
expression omnibus; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; OS: overall survival; PBMC: peripheral blood mononuclear cell; PFS: progression-free
survival; TCGA: the cancer genome atlas; TNM: tumour node metastasis
are decreased in stage IV lung and breast cancers , and are lower in stage III/IV than in stage I/II lung
[88]
[89]
cancer patients . By contrast, the presence of anti-a-enolase antibodies in sera from chronic lymphocytic
[90]
leukaemia (CLL) patients is predictive of a shorter time to first treatment , indicating that the presence
of a-enolase antibodies are indicative of a disrupted immune system in CLL. Taken together, these studies
suggest that autoantibodies against a-enolase are a good prognostic factor in pancreatic, lung and breast
cancers, and provide further evidence that targeting a-enolase may be beneficial in solid tumours.
ENOLASE INHIBITORS ARE POTENTIAL ANTICANCER AGENTS
Due to its important cancer-related roles, enolase is one of several glycolytic enzymes being examined as
a potential anticancer therapeutic target. Polyamine sulphonamide analogues have proven particularly
effective at inhibiting a-enolase activity. Two such compounds have been further developed and shown to