Page 112 - Read Online
P. 112
Schofield et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:10 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.43 Page 7 of 12
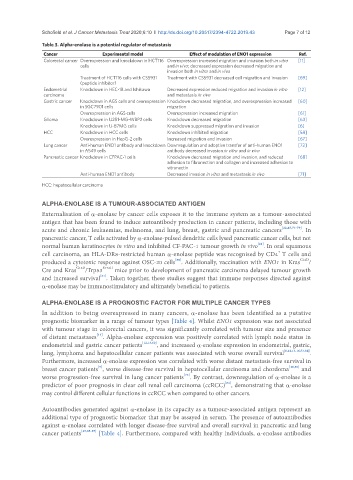
Table 3. Alpha-enolase is a potential regulator of metastasis
Cancer Experimental model Effect of modulation of ENO1 expression Ref.
Colorectal cancer Overexpression and knockdown in HCT116 Overexpression increased migration and invasion both in vitro [11]
cells and in vivo; decreased expression decreased migration and
invasion both in vitro and in vivo
Treatment of HCT116 cells with CS5931 Treatment with CS5931 decreased cell migration and invasion [69]
(peptide inhibitor)
Endometrial Knockdown in HEC-1B and Ishikawa Decreased expression reduced migration and invasion in vitro [12]
carcinoma and metastasis in vivo
Gastric cancer Knockdown in AGS cells and overexpression Knockdown decreased migration, and overexpression increased [60]
in SGC7901 cells migration
Overexpression in AGS cells Overexpression increased migration [61]
Glioma Knockdown in U251-MG-WBP2 cells Knockdown decreased migration [63]
Knockdown in U-87MG cells Knockdown suppressed migration and invasion [6]
HCC Knockdown in HCC cells Knockdown inhibited migration [58]
Overexpression in HepG-2 cells Increased migration and invasion [67]
Lung cancer Anti-human ENO1 antibody and knockdown Downregulation and adoptive transfer of anti-human ENO1 [72]
in A549 cells antibody decreased invasion in vitro and in vivo
Pancreatic cancer Knockdown in CFPAC-1 cells Knockdown decreased migration and invasion, and reduced [68]
adhesion to fibronection and collagen and increased adhesion to
vitronectin
Anti-human ENO1 antibody Decreased invasion in vitro and metastasis in vivo [71]
HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma
ALPHA-ENOLASE IS A TUMOUR-ASSOCIATED ANTIGEN
Externalisation of a-enolase by cancer cells exposes it to the immune system as a tumour-associated
antigen that has been found to induce autoantibody production in cancer patients, including those with
acute and chronic leukaemias, melanoma, and lung, breast, gastric and pancreatic cancers [22,45,73-79] . In
pancreatic cancer, T cells activated by a-enolase-pulsed dendritic cells lysed pancreatic cancer cells, but not
normal human keratinocytes in vitro and inhibited CF-PAC-1 tumour growth in vivo . In oral squamous
[22]
+
cell carcinoma, an HLA-DR8-restricted human a-enolase peptide was recognised by CD4 T cells and
produced a cytotoxic response against OSC-20 cells . Additionally, vaccination with ENO1 in Kras G12D /
[80]
Cre and Kras G12D /Trp53 R172H mice prior to development of pancreatic carcinoma delayed tumour growth
and increased survival . Taken together, these studies suggest that immune responses directed against
[81]
a-enolase may be immunostimulatory and ultimately beneficial to patients.
ALPHA-ENOLASE IS A PROGNOSTIC FACTOR FOR MULTIPLE CANCER TYPES
In addition to being overexpressed in many cancers, a-enolase has been identified as a putative
prognostic biomarker in a range of tumour types [Table 4]. Whilst ENO1 expression was not associated
with tumour stage in colorectal cancers, it was significantly correlated with tumour size and presence
[11]
of distant metastases . Alpha-enolase expression was positively correlated with lymph node status in
endometrial and gastric cancer patients [12,13,60] , and increased a-enolase expression in endometrial, gastric,
lung, lymphoma and hepatocellular cancer patients was associated with worse overall survival [8,12,13,16,73,82] .
Furthermore, increased a-enolase expression was correlated with worse distant metastasis-free survival in
[9]
breast cancer patients , worse disease-free survival in hepatocellular carcinoma and chordoma [16,83] and
[73]
worse progression-free survival in lung cancer patients . By contrast, downregulation of a-enolase is a
[84]
predictor of poor prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) , demonstrating that a-enolase
may control different cellular functions in ccRCC when compared to other cancers.
Autoantibodies generated against a-enolase in its capacity as a tumour-associated antigen represent an
additional type of prognostic biomarker that may be assayed in serum. The presence of autoantibodies
against a-enolase correlated with longer disease-free survival and overall survival in pancreatic and lung
cancer patients [45,85-87] [Table 4]. Furthermore, compared with healthy individuals, a-enolase antibodies