Page 289 - Read Online
P. 289
Bracht et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:22 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.111 Page 3 of 10
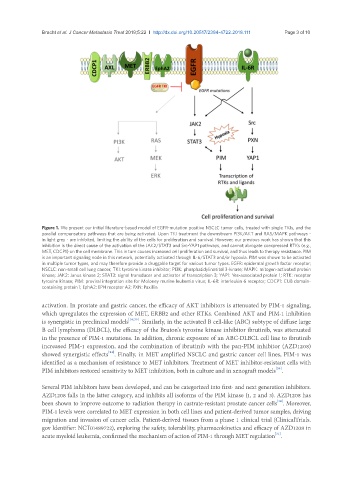
Figure 1. We present our initial literature-based model of EGFR-mutation positive NSCLC tumor cells, treated with single TKIs, and the
parallel compensatory pathways that are being activated. Upon TKI treatment the downstream PI3K/AKT and RAS/MAPK pathways -
in light grey - are inhibited, limiting the ability of the cells for proliferation and survival. However, our previous work has shown that this
inhibition is the direct cause of the activation of the JAK2/STAT3 and Src-YAP1 pathways, and cannot abrogate coexpressed RTKs (e.g.,
MET, CDCP1) on the cell membrane. This in turn causes increased cell proliferation and survival, and thus leads to therapy resistance. PIM
is an important signaling node in this network, potentially activated through IL-6/STAT3 and/or hypoxia. PIM was shown to be activated
in multiple tumor types, and may therefore provide a druggable target for various tumor types. EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor;
NSCLC: non-small cell lung cancer; TKI: tyrosine kinase inhibitor; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein
kinase; JAK2: Janus kinase 2; STAT3: signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; YAP1: Yes-associated protein 1; RTK: receptor
tyrosine kinase; PIM: proviral integration site for Moloney murine leukemia virus; IL-6R: interleukin 6 receptor; CDCP1: CUB domain-
containing protein 1; EphA2: EPH receptor A2; PXN: Paxillin
activation. In prostate and gastric cancer, the efficacy of AKT inhibitors is attenuated by PIM-1 signaling,
which upregulates the expression of MET, ERBB2 and other RTKs. Combined AKT and PIM-1 inhibition
is synergistic in preclinical models [16,30] . Similarly, in the activated B cell-like (ABC) subtype of diffuse large
B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the efficacy of the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib, was attenuated
in the presence of PIM-1 mutations. In addition, chronic exposure of an ABC-DLBCL cell line to ibrutinib
increased PIM-1 expression, and the combination of ibrutinib with the pan-PIM inhibitor (AZD1208)
[24]
showed synergistic effects . Finally, in MET amplified NSCLC and gastric cancer cell lines, PIM-1 was
identified as a mechanism of resistance to MET inhibitors. Treatment of MET inhibitor-resistant cells with
[26]
PIM inhibitors restored sensitivity to MET inhibition, both in culture and in xenograft models .
Several PIM inhibitors have been developed, and can be categorized into first- and next generation inhibitors.
AZD1208 falls in the latter category, and inhibits all isoforms of the PIM kinase (1, 2 and 3). AZD1208 has
[14]
been shown to improve outcome to radiation therapy in castrate-resistant prostate cancer cells . Moreover,
PIM-1 levels were correlated to MET expression in both cell lines and patient-derived tumor samples, driving
migration and invasion of cancer cells. Patient-derived tissues from a phase 1 clinical trial (ClinicalTrials.
gov Identifier: NCT01489722), exploring the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and efficacy of AZD1208 in
acute myeloid leukemia, confirmed the mechanism of action of PIM-1 through MET regulation .
[31]