Page 140 - Read Online
P. 140
Page 12 of 18 Wallace et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:9 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.01
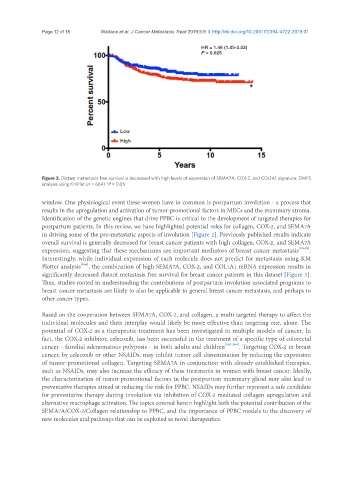
HR = 1.46 (1.05-2.03)
P = 0.025
Low
High
Figure 3. Distant metastasis free survival is decreased with high levels of expression of SEMA7A, COX-2, and COL1A1 signature. DMFS
analysis using KmPlot (n = 664) *P < 0.05
window. One physiological event these women have in common is postpartum involution - a process that
results in the upregulation and activation of tumor-promotional factors in MECs and the mammary stroma.
Identification of the genetic engines that drive PPBC is critical to the development of targeted therapies for
postpartum patients. In this review, we have highlighted potential roles for collagen, COX-2, and SEMA7A
in driving some of the pro-metastatic aspects of involution [Figure 2]. Previously published results indicate
overall survival is generally decreased for breast cancer patients with high collagen, COX-2, and SEMA7A
expression, suggesting that these mechanisms are important mediators of breast cancer metastasis [18,49] .
Interestingly, while individual expression of each molecule does not predict for metastasis using KM
Plotter analysis [166] , the combination of high SEMA7A, COX-2, and COL1A1 mRNA expression results in
significantly decreased distant metastasis free survival for breast cancer patients in this dataset [Figure 3].
Thus, studies rooted in understanding the contributions of postpartum involution associated programs to
breast cancer metastasis are likely to also be applicable to general breast cancer metastasis, and perhaps to
other cancer types.
Based on the cooperation between SEMA7A, COX-2, and collagen, a multi-targeted therapy to affect the
individual molecules and their interplay would likely be more effective than targeting one, alone. The
potential of COX-2 as a therapeutic treatment has been investigated in multiple models of cancer. In
fact, the COX-2 inhibitor, celecoxib, has been successful in the treatment of a specific type of colorectal
cancer - familial adenomatous polyposis - in both adults and children [167,168] . Targeting COX-2 in breast
cancer, by celecoxib or other NSAIDs, may inhibit tumor cell dissemination by reducing the expression
of tumor-promotional collagen. Targeting SEMA7A in conjunction with already established therapies,
such as NSAIDs, may also increase the efficacy of these treatments in women with breast cancer. Ideally,
the characterization of tumor-promotional factors in the postpartum mammary gland may also lead to
preventative therapies aimed at reducing the risk for PPBC. NSAIDs may further represent a safe candidate
for preventative therapy during involution via inhibition of COX-2 mediated collagen upregulation and
alternative macrophage activation. The topics covered herein highlight both the potential contribution of the
SEMA7A/COX-2/Collagen relationship to PPBC, and the importance of PPBC models to the discovery of
new molecules and pathways that can be exploited as novel therapeutics.