Page 50 - Read Online
P. 50
Paridar et al. BCR-ABL and myelodysplastic syndrome
Hematological
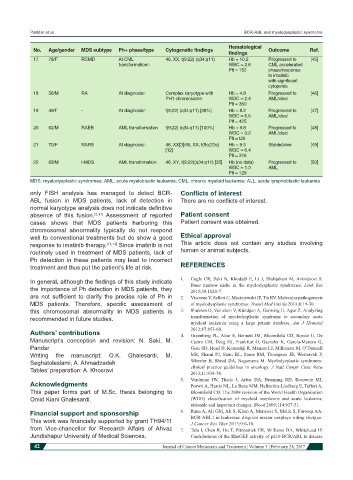
No. Age/gender MDS subtype Ph+ phase/type Cytogenetic findings Outcome Ref.
findings
17 78/F RCMD At CML 46, XX, t(9;22) (q34;q11) Hb = 10.2 Progressed to [45]
transformation/- WBC = 2.6 CML accelerated
Plt = 152 phase/response
to imatinib
with significant
cytopenia
18 56/M RA At diagnosis/- Complex karyotype with Hb = 4.8 Progressed to [46]
PH1 chromosome WBC = 2.4 AML/died
Plt = 350
19 49/F - At diagnosis/- t(9;22) (q34;q11) [38%] Hb = 8.2 Progressed to [47]
WBC = 6.5 AML/died
Plt = 425
20 62/M RAEB AML transformation t(9;22) (q34:q11) [100%] Hb = 9.8 Progressed to [48]
WBC = 3.2 AML/died
Plt =120
21 70/F RARS At diagnosis/- 46, XX[3]/46, XX, t(9q;22q) Hb = 9.5 Stable/alive [49]
[12] WBC = 6.4
Plt = 316
22 69/M t-MDS AML transfomation 46, XY, t(9;22)(q34;q11) [35] Hb (no data) Progressed to [50]
WBC = 1.3 AML
Plt = 129
MDS: myelodysplastic syndromes; AML: acute myeloblastic leukemia; CML: chronic myeloid leukemia; ALL: acute lymphoblastic leukemia
only FISH analysis has managed to detect BCR- Conflicts of interest
ABL fusion in MDS patients, lack of detection in There are no conflicts of interest.
normal karyotype analysis does not indicate definitive
absence of this fusion. [5,11] Assessment of reported Patient consent
cases shows that MDS patients harboring this Patient consent was obtained.
chromosomal abnormality typically do not respond
well to conventional treatments but do show a good Ethical approval
response to imatinib therapy. [11,13] Since imatinib is not This article does not contain any studies involving
routinely used in treatment of MDS patients, lack of human or animal subjects.
Ph detection in these patients may lead to incorrect
treatment and thus put the patient’s life at risk. REFERENCES
In general, although the findings of this study indicate 1. Cogle CR, Saki N, Khodadi E, Li J, Shahjahani M, Azizidoost S.
Bone marrow niche in the myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk Res
the importance of Ph detection in MDS patients, they 2015;39:1020-7.
are not sufficient to clarify the precise role of Ph in 2. Visconte V, Selleri C, Maciejewski JP, Tiu RV. Molecular pathogenesis
MDS patients. Therefore, specific assessment of of myelodysplastic syndromes. Transl Med Uni Sa 2014;8:19-30.
this chromosomal abnormality in MDS patients is 3. Shukron O, Vainstein V, Kündgen A, Germing U, Agur Z. Analyzing
recommended in future studies. transformation of myelodysplastic syndrome to secondary acute
myeloid leukemia using a large patient database. Am J Hematol
Authors’ contributions 4. 2012;87:853-60.
Greenberg PL, Attar E, Bennett JM, Bloomfield CD, Borate U, De
Manuscript’s conception and revision: N. Saki, M. Castro CM, Deeg HJ, Frankfurt O, Gaensler K, Garcia-Manero G,
Paridar Gore SD, Head D, Komrokji R, Maness LJ, Millenson M, O’Donnell
Writing the manuscript: O.K. Ghalesardi, M. MR, Shami PJ, Stein BL, Stone RM, Thompson JE, Westervelt P,
Seghatoleslami, A. Ahmadzadeh Wheeler B, Shead DA, Naganuma M. Myelodysplastic syndromes:
Tables’ preparation: A. Khosravi clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw
2013;11:838-74.
5. Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, Brunning RD, Borowitz MJ,
Acknowledgments Porwit A, Harris NL, Le Beau MM, Hellström-Lindberg E, Tefferi A,
This paper forms part of M.Sc. thesis belonging to Bloomfield CD. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization
Omid Kiani Ghalesardi. (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia:
rationale and important changes. Blood 2009;114:937-51.
Financial support and sponsorship 6. Rana A, Ali GM, Ali S, Khan A, Mansoor S, Malik S, Farooqi AA.
This work was financially supported by grant TH94/11 BCR-ABL1 in leukemia: disguise master outplays riding shotgun.
J Cancer Res Ther 2013;9:6-10.
from Vice-chancellor for Research Affairs of Ahvaz 7. Tala I, Chen R, Hu T, Fitzpatrick ER, Williams DA, Whitehead IP.
Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences. Contributions of the RhoGEF activity of p210 BCR/ABL to disease
42 Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 3 ¦ February 28, 2017