Page 454 - Read Online
P. 454
Poddar et al. Carcinoma tongue in renal transplant recipient
of head, generalized itching, low urine output, and
generalized edema for one month. Upon investigation,
he was found to have chronic kidney disease involving
mainly the left kidney. It was advised that the patient
undergo renal transplant but this was refused by the
parents due to financial constraints. The child was
kept on supportive care and follow up. At the age of
18, he finally underwent transplant due to worsening
of renal function (1998). He was then put ona
azathioprine, prednisolone and cyclosporine regimen
for immunosuppression following transplantation.
Cyclosporine was discontinued after two years
and the patient was continued on azathioprine and
prednisolone. He was on regular follow-up since after,
with no major complaints. In 2010, he developed
hepatitis B and C co-infection and was placed on
Tenofovir. In 2016, 18 years after transplantation and
being on immunosuppressive therapy, he developed
an ulcer on the tongue. On biopsy, it was found to be
a squamous cell carcinoma. Computed tomography
scan (22/04/2016) showed ill defined, hyperdense
lesion, 16 mm × 6 mm in size, involving the anterior
aspect of left lateral border of the tongue, not crossing
midline or involving the base of tongue or vallecula.
There were few subcentimeter lymph nodes on the
left, level Ib and II. On history, the patient had no
history of chewing tobacco, smoking, or use of alcohol.
Also, there was no history suggestive offactors, which
could have led to chronic irritationand subsequently
to malignancy. On 22/03/2016, he underwent surgical
treatment (left partial glossectomy and left modified
neck dissection). Histopathology report was squamous
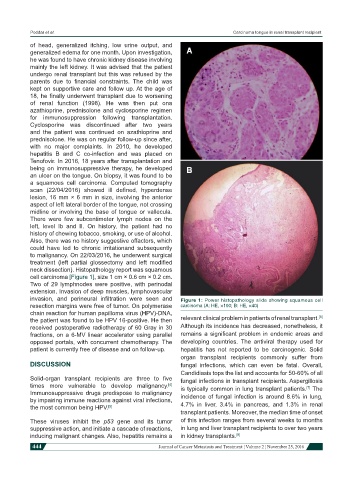
cell carcinoma [Figure 1], size 1 cm × 0.6 cm × 0.2 cm.
Two of 29 lymphnodes were positive, with perinodal
extension. Invasion of deep muscles, lymphovascular
invasion, and perineural infiltration were seen and Figure 1: Power histopathology slide showing squamous cell
resection margins were free of tumor. On polymerase carcinoma (A: HE, ×100; B: HE, ×40)
chain reaction for human papilloma virus (HPV)-DNA,
[6]
the patient was found to be HPV 16-positive. He then relevant clinical problem in patients of renal transplant.
received postoperative radiotherapy of 60 Gray in 30 Although its incidence has decreased, nonetheless, it
fractions, on a 6-MV linear accelerator using parallel remains a significant problem in endemic areas and
opposed portals, with concurrent chemotherapy. The developing countries. The antiviral therapy used for
patient is currently free of disease and on follow-up. hepatitis has not reported to be carcinogenic. Solid
organ transplant recipients commonly suffer from
DISCUSSION fungal infections, which can even be fatal. Overall,
Candidiasis tops the list and accounts for 50-60% of all
Solid-organ transplant recipients are three to five fungal infections in transplant recipients. Aspergillosis
times more vulnerable to develop malignancy. is typically common in lung transplant patients. The
[4]
[7]
Immunosuppressive drugs predispose to malignancy incidence of fungal infection is around 8.6% in lung,
by impairing immune reactions against viral infections,
the most common being HPV. [5] 4.7% in liver, 3.4% in pancreas, and 1.3% in renal
transplant patients. Moreover, the median time of onset
These viruses inhibit the p53 gene and its tumor of this infection ranges from several weeks to months
suppressive action, and initiate a cascade of reactions, in lung and liver transplant recipients to over two years
inducing malignant changes. Also, hepatitis remains a in kidney transplants. [8]
444 Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 2 ¦ November 25, 2016