Page 208 - Read Online
P. 208
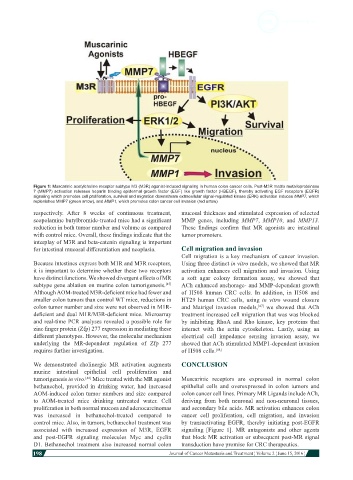
Figure 1: Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtype M3 (M3R) agonist-induced signaling in human colon cancer cells. Post-M3R matrix metalloproteinase
7 (MMP7) activation releases heparin binding epidermal growth factor (EGF) like growth factor (HBEGF), thereby activating EGF receptors (EGFR)
signaling which promotes cell proliferation, survival and migration downstream extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation induces MMP7, which
replenishes MMP7 (green arrow), and MMP1, which promotes colon cancer cell invasion (red arrow)
respectively. After 8 weeks of continuous treatment, mucosal thickness and stimulated expression of selected
scopolamine butylbromide-treated mice had a significant MMP genes, including MMP7, MMP10, and MMP13.
reduction in both tumor number and volume as compared These findings confirm that MR agonists are intestinal
with control mice. Overall, these findings indicate that the tumor promoters.
interplay of M3R and beta-catenin signaling is important
for intestinal mucosal differentiation and neoplasia. Cell migration and invasion
Cell migration is a key mechanism of cancer invasion.
Because intestines express both M1R and M3R receptors, Using three distinct in vitro models, we showed that MR
it is important to determine whether these two receptors activation enhances cell migration and invasion. Using
have distinct functions. We showed divergent effects of MR a soft agar colony formation assay, we showed that
subtype gene ablation on murine colon tumorigenesis. ACh enhanced anchorage- and MMP-dependent growth
[45]
Although AOM-treated M3R-deficient mice had fewer and of H508 human CRC cells. In addition, in H508 and
smaller colon tumors than control WT mice, reductions in HT29 human CRC cells, using in vitro wound closure
colon tumor number and size were not observed in M1R- and Matrigel invasion models, [47] we showed that ACh
deficient and dual M1R/M3R-deficient mice. Microarray treatment increased cell migration that was was blocked
and real-time PCR analyses revealed a possible role for by inhibiting RhoA and Rho kinase, key proteins that
zinc finger protein (Zfp) 277 expression in mediating these interact with the actin cytoskeleton. Lastly, using an
different phenotypes. However, the molecular mechanism electrical cell impedance sensing invasion assay, we
underlying the MR-dependent regulation of Zfp 277 showed that ACh stimulated MMP1-dependent invasion
requires further investigation. of H508 cells. [48]
We demonstrated cholinergic MR activation augments CONCLUSION
murine intestinal epithelial cell proliferation and
tumorigenesis in vivo. Mice treated with the MR agonist Muscarinic receptors are expressed in normal colon
[46]
bethanechol, provided in drinking water, had increased epithelial cells and overexpressed in colon tumors and
AOM-induced colon tumor numbers and size compared colon cancer cell lines. Primary MR Ligands include ACh,
to AOM-treated mice drinking untreated water. Cell deriving from both neuronal and non-neuronal tissues,
proliferation in both normal mucosa and adenocarcinomas and secondary bile acids. MR activation enhances colon
was increased in bethanechol-treated compared to cancer cell proliferation, cell migration, and invasion
control mice. Also, in tumors, bethanechol treatment was by transactivating EGFR, thereby initiating post-EGFR
associated with increased expression of M3R, EGFR signaling [Figure 1]. MR antagonists and other agents
and post-EGFR signaling molecules Myc and cyclin that block MR activation or subsequent post-MR signal
D1. Bethanechol treatment also increased normal colon transduction have promise for CRC therapeutics.
198
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 2 ¦ June 15, 2016 ¦