Page 151 - Read Online
P. 151
the treatment. The time taken for every treatment was also Table 1: Combined uterine motion in three different
similar among the patients undergoing IGRT of the pelvic dimensions in patients undergoing radiotherapy
region. The Mean of all the obtained-values for each patient Dimensions Mean (SD), Median, Range of
was calculated and an unpaired-one-sample student t-test cm cm motion, cm
was applied to obtain the significance. The P value is less Lateral (X) 0.23 (0.22) 0.2 - 0.6 to 0.45
than 0.001 which is highly significant. Anteroposterior (Y) 0.67 (0.83) 0.57 - 2.28 to 1.3
Superoinferior (Z) 0.29 (0.40) 0.245 - 0.36 to 0.71
RESULTS
present, was minimum. The posterior shift might be due to
The mean, standard deviation, and median of uterine motion the rectal filling or presence or absence of gas in the rectum.
in each plane were calculated to see its association with the
bladder filling and its influence on the displacement of the The mean bladder volume was calculated to be 90.55 mL
uterus. As shown in the Table 1, the displacement ranges for all patients, and each patient had an average bladder
were significant depending on the patient, although the volume of about 80 mL to 100 mL over the course of their
mean values of the displacement were within 1 cm. The treatment. This was done by maintaining a strict bladder
mean values of shift in AP, SI, and lateral directions were control protocol for each patient. We found that maximum
respectively 0.67, 0.29, and 0.23 for all the 96 scans done range of motion was observed when the bladder volume
for 24 patients over the period of EBRT [Table 2]. exceeded 100 mL as was seen in patient number 4, where
a mean maximum shift in AP direction was almost up to
The mean extent of motion in the uterine position on a daily -2.8 cm. When it was compared with their mean bladder
basis for individual patients ranged from -2.28 to +1.3 in volume, it was found to be excessive with a mean of almost
AP, -0.56 to +0.71 in SI, and from -0.6 to +0.45 in lateral up to 180 mL during the course of their treatment.
directions. The mean movement in all the directions was
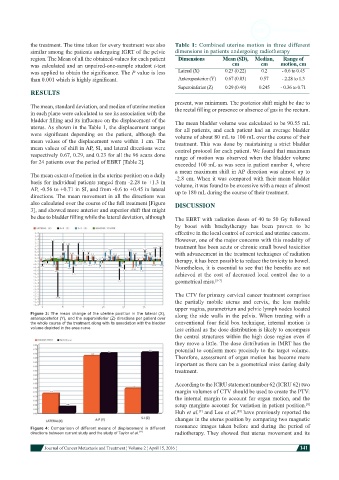
also calculated over the course of the full treatment [Figure DISCUSSION
3], and showed more anterior and superior shift that might
be due to bladder filling while the lateral deviation, although The EBRT with radiation doses of 40 to 50 Gy followed
by boost with brachytherapy has been proven to be
effective in the local control of cervical and uterine cancers.
However, one of the major concerns with this modality of
treatment has been acute or chronic small bowel toxicities
with advancement in the treatment techniques of radiation
therapy, it has been possible to reduce the toxicity to bowel.
Nonetheless, it is essential to see that the benefits are not
achieved at the cost of decreased local control due to a
geometrical miss. [5-7]
The CTV for primary cervical cancer treatment comprises
the partially mobile uterus and cervix, the less mobile
upper vagina, parametrium and pelvic lymph nodes located
Figure 3: The mean change of the uterine position in the lateral (X), along the side walls in the pelvis. When treating with a
anteroposterior (Y), and the superoinferior (Z) directions per patient over
the whole course of the treatment along with its association with the bladder conventional four field box technique, internal motion is
volume depicted in the area curve less critical as the dose distribution is likely to encompass
the central structures within the high dose region even if
they move a little. The dose distribution in IMRT has the
potential to conform more precisely to the target volume.
Therefore, assessment of organ motion has become more
important as there can be a geometrical miss during daily
treatment.
According to the ICRU statement number 62 (ICRU 62) two
margin volumes of CTV should be used to create the PTV:
the internal margin to account for organ motion, and the
setup marginto account for variation in patient position. [8]
Huh et al. and Lee et al. [10] have previously reported the
[9]
changes in the uterus position by comparing two magnetic
resonance images taken before and during the period of
Figure 4: Comparison of different means of displacement in different
directions between current study and the study of Taylor et al. [11] radiotherapy. They showed that uterus movement and its
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 2 ¦ April 15, 2016 ¦ 141