Page 39 - Read Online
P. 39
a b c
d e
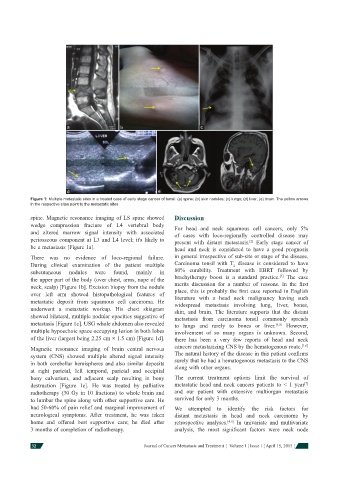
Figure 1: Multiple metastatic sites in a treated case of early stage cancer of tonsil: (a) spine; (b) skin nodules; (c) lungs; (d) liver; (e) brain. The yellow arrows
in the respective sites point to the metastatic sites
spine. Magnetic resonance imaging of LS spine showed Discussion
wedge compression fracture of L4 vertebral body For head and neck squamous cell cancers, only 5%
and altered marrow signal intensity with associated of cases with loco-regionally controlled disease may
periosseous component at L3 and L4 level; it's likely to present with distant metastasis. Early stage cancer of
[2]
be a metastasis [Figure 1a]. head and neck is considered to have a good prognosis
There was no evidence of loco-regional failure. in general irrespective of sub-site or stage of the disease.
During clinical examination of the patient multiple Carcinoma tonsil with T disease is considered to have
2
subcutaneous nodules were found, mainly in 80% curability. Treatment with EBRT followed by
[3]
the upper part of the body (over chest, arms, nape of the brachytherapy boost is a standard practice. The case
neck, scalp) [Figure 1b]. Excision biopsy from the nodule merits discussion for a number of reasons. In the fi rst
over left arm showed histopathological features of place, this is probably the fi rst case reported in English
literature with a head neck malignancy having such
metastatic deposit from squamous cell carcinoma. He widespread metastasis involving lung, liver, bones,
underwent a metastatic workup. His chest skiagram skin, and brain. The literature supports that the distant
showed bilateral, multiple nodular opacities suggestive of metastasis from carcinoma tonsil commonly spreads
metastasis [Figure 1c]. USG whole abdomen also revealed to lungs and rarely to bones or liver. [4,5] However,
multiple hypoechoic space occupying lesion in both lobes involvement of so many organs is unknown. Second,
of the liver (largest being 2.25 cm × 1.5 cm) [Figure 1d]. there has been a very few reports of head and neck
Magnetic resonance imaging of brain central nervous cancers metastasizing CNS by the hematogenous route. [1,6]
system (CNS) showed multiple altered signal intensity The natural history of the disease in this patient confi rms
in both cerebellar hemispheres and also similar deposits surely that he had a hematogenous metastasis to the CNS
at right parietal, left temporal, parietal and occipital along with other organs.
bony calvarium, and adjacent scalp resulting in bony The current treatment options limit the survival of
[7]
destruction [Figure 1e]. He was treated by palliative metastatic head and neck cancers patients to < 1 year
radiotherapy (30 Gy in 10 fractions) to whole brain and and our patient with extensive multiorgan metastasis
to lumbar the spine along with other supportive care. He survived for only 3 months.
had 50-60% of pain relief and marginal improvement of We attempted to identify the risk factors for
neurological symptoms. After treatment, he was taken distant metastasis in head and neck carcinoma by
home and offered best supportive care; he died after retrospective analyses. [4,8] In univariate and multivariate
3 months of completion of radiotherapy. analysis, the most signifi cant factors were neck node
32 Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 1 ¦ Issue 1 ¦ April 15, 2015 ¦