Page 36 - Read Online
P. 36
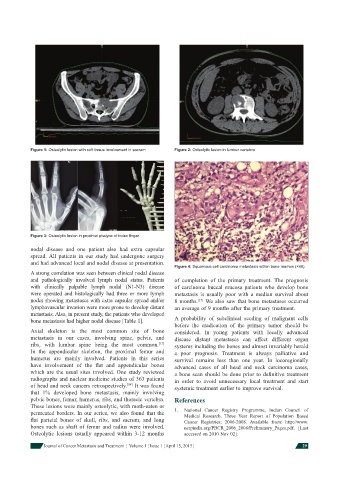
Figure 1: Osteolytic lesion with soft tissue involvement in sacrum Figure 2: Osteolytic lesion in lumber vertebra
Figure 3: Osteolytic lesion in proximal phalynx of index fi nger
nodal disease and one patient also had extra capsular
spread. All patients in our study had undergone surgery
and had advanced local and nodal disease at presentation.
Figure 4: Squamous cell carcinoma metastasis within bone marrow (×40)
A strong correlation was seen between clinical nodal disease
and pathologically involved lymph nodal status. Patients of completion of the primary treatment. The prognosis
with clinically palpable lymph nodal (N1-N3) disease of carcinoma buccal mucosa patients who develop bone
were operated and histologically had three or more lymph metastasis is usually poor with a median survival about
nodes showing metastases with extra capsular spread and/or 8 months. We also saw that bone metastases occurred
[15]
lymphovascular invasion were more prone to develop distant an average of 9 months after the primary treatment.
metastasis. Also, in present study, the patients who developed
bone metastasis had higher nodal disease [Table 1]. A probability of subclinical seeding of malignant cells
before the eradication of the primary tumor should be
Axial skeleton is the most common site of bone considered. In young patients with locally advanced
metastasis in our cases, involving spine, pelvis, and disease distant metastases can affect different organ
ribs, with lumbar spine being the most common. systems including the bones and almost invariably herald
[13]
In the appendicular skeleton, the proximal femur and a poor prognosis. Treatment is always palliative and
humerus are mainly involved. Patients in this series survival remains less than one year. In locoregionally
have involvement of the fl at and appendicular bones advanced cases of all head and neck carcinoma cases,
which are the usual sites involved. One study reviewed a bone scan should be done prior to defi nitive treatment
radiographs and nuclear medicine studies of 363 patients in order to avoid unnecessary local treatment and start
of head and neck cancers retrospectively. It was found systemic treatment earlier to improve survival.
[14]
that 1% developed bone metastasis, mainly involving
pelvic bones, femur, humerus, ribs, and thoracic vertebra. References
These lesions were mainly osteolytic, with moth-eaten or
permeated borders. In our series, we also found that the 1. National Cancer Registry Programme, Indian Council of
Medical Research. Three Year Report of Population Based
fl at parietal bones of skull, ribs, and sacrum, and long Cancer Registries; 2006-2008. Available from: http://www.
bones such as shaft of femur and radius were involved. ncrpindia.org/PBCR_2006_2008/Preliminary_Pages.pdf. [Last
Osteolytic lesions usually appeared within 3-12 months accessed on 2010 Nov 02].
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 1 ¦ Issue 1 ¦ April 15, 2015 ¦ 29