Page 69 - Read Online
P. 69
Lee et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2021;7:27 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2021.58 Page 9 of 18
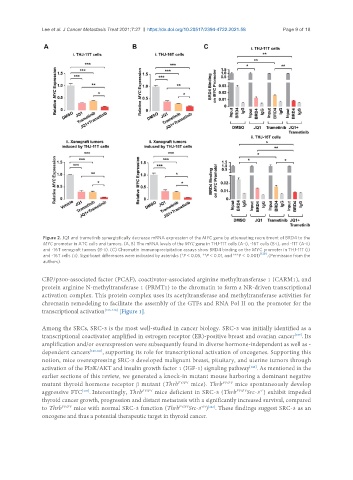
Figure 2. JQ1 and trametinib synergistically decrease mRNA expression of the MYC gene by attenuating recruitment of BRD4 to the
MYC promoter in ATC cells and tumors. (A, B) The mRNA levels of the MYC gene in THJ-11T cells (A-i), -16T cells (B-i), and -11T (A-ii)
and -16T xenograft tumors (B-ii). (C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays show BRD4 binding on the MYC promoter in THJ-11T (i)
and -16T cells (ii). Significant differences were indicated by asterisks (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001) [129] . (Permission from the
authors).
CBP/p300-associated factor (PCAF), coactivator-associated arginine methyltransferase 1 (CARM1), and
protein arginine N-methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1) to the chromatin to form a NR-driven transcriptional
activation complex. This protein complex uses its acetyltransferase and methyltransferase activities for
chromatin remodeling to facilitate the assembly of the GTFs and RNA Pol II on the promoter for the
transcriptional activation [133-138] [Figure 1].
Among the SRCs, SRC-3 is the most well-studied in cancer biology. SRC-3 was initially identified as a
transcriptional coactivator amplified in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast and ovarian cancer . Its
[139]
amplification and/or overexpression were subsequently found in diverse hormone-independent as well as -
dependent cancers [140,141] , supporting its role for transcriptional activation of oncogenes. Supporting this
notion, mice overexpressing SRC-3 developed malignant breast, pituitary, and uterine tumors through
activation of the PI3K/AKT and insulin growth factor 1 (IGF-1) signaling pathway . As mentioned in the
[142]
earlier sections of this review, we generated a knock-in mutant mouse harboring a dominant negative
mutant thyroid hormone receptor β mutant (Thrb PV/PV mice). Thrb PV/PV mice spontaneously develop
aggressive FTC . Interestingly, Thrb PV/PV mice deficient in SRC-3 (Thrb PV/PV Src-3 ) exhibit impeded
-/-
[103]
thyroid cancer growth, progression and distant metastasis with a significantly increased survival, compared
to Thrb PV/PV mice with normal SRC-3 function (Thrb PV/PV Src-3 ) . These findings suggest SRC-3 as an
+/+ [143]
oncogene and thus a potential therapeutic target in thyroid cancer.