Page 107 - Read Online
P. 107
Page 10 of 19 Davidson et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2021;7:45 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2021.77
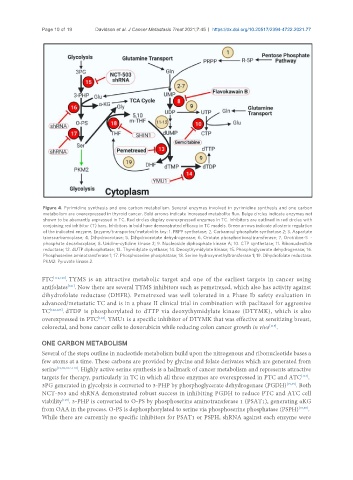
Figure 4. Pyrimidine synthesis and one carbon metabolism. Several enzymes involved in pyrimidine synthesis and one carbon
metabolism are overexpressed in thyroid cancer. Bold arrows indicate increased metabolite flux. Beige circles indicate enzymes not
shown to be aberrantly expressed in TC. Red circles display overexpressed enzymes in TC. Inhibitors are outlined in red circles with
conjoining red inhibitor (T) bars. Inhibitors in bold have demonstrated efficacy in TC models. Green arrows indicate allosteric regulation
of the indicated enzyme. Enzyme/transporter/metabolite key: 1. PRPP synthetase; 2. Carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase 2; 3. Aspartate
transcarbamoylase; 4. Dihydroorotase; 5. Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase; 6. Orotate phosphoribosyltransferase; 7. Orotidine-5 -
phosphate decarboxylase; 8. Uridine-cytidine kinase 2; 9. Nucleoside diphosphate kinase A; 10. CTP synthetase; 11. Ribonucleotide
reductase; 12. dUTP diphosphatase; 13. Thymidylate synthase; 14. Deoxythymidylate kinase; 15. Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase; 16.
Phosphoserine aminotransferase 1; 17. Phosphoserine phosphatase; 18. Serine hydroxymethyltransferase 1; 19. Dihydrofolate reductase.
PKM2: Pyruvate kinase 2.
FTC [112,120] . TYMS is an attractive metabolic target and one of the earliest targets in cancer using
[121]
antifolates . Now there are several TYMS inhibitors such as pemetrexed, which also has activity against
dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR). Pemetrexed was well tolerated in a Phase Ib safety evaluation in
advanced/metastatic TC and is in a phase II clinical trial in combination with paclitaxel for aggressive
TC [122,123] . dTDP is phosphorylated to dTTP via deoxythymidylate kinase (DTYMK), which is also
overexpressed in PTC . YMU1 is a specific inhibitor of DTYMK that was effective at sensitizing breast,
[112]
colorectal, and bone cancer cells to doxorubicin while reducing colon cancer growth in vivo .
[119]
ONE CARBON METABOLISM
Several of the steps outline in nucleotide metabolism build upon the nitrogenous and ribonucleotide bases a
few atoms at a time. These carbons are provided by glycine and folate derivates which are generated from
serine [15,35,107-110] . Highly active serine synthesis is a hallmark of cancer metabolism and represents attractive
targets for therapy, particularly in TC in which all three enzymes are overexpressed in PTC and ATC .
[124]
3PG generated in glycolysis is converted to 3-PHP by phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (PGDH) [15,35] . Both
NCT-503 and shRNA demonstrated robust success in inhibiting PGDH to reduce PTC and ATC cell
viability . 3-PHP is converted to O-PS by phosphoserine aminotransferase 1 (PSAT1), generating αKG
[125]
from OAA in the process. O-PS is dephosphorylated to serine via phosphoserine phosphatase (PSPH) [15,35] .
While there are currently no specific inhibitors for PSAT1 or PSPH, shRNA against each enzyme were