Page 59 - Read Online
P. 59
Karolak et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2021;7:15 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2021.05 Page 3 of 16
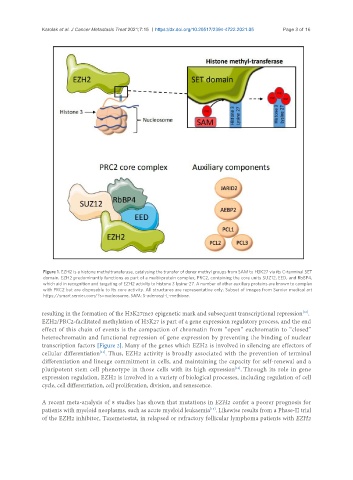
Figure 1. EZH2 is a histone methyltransferase, catalysing the transfer of donor methyl groups from SAM to H3K27 via its C-terminal SET
domain. EZH2 predominantly functions as part of a multi-protein complex, PRC2, containing the core units SUZ12, EED, and RbBP4,
which aid in recognition and targeting of EZH2 activity to histone 3 lysine-27. A number of other auxiliary proteins are known to complex
with PRC2 but are disposable to its core activity. All structures are representative only. Subset of images from Servier medical art
https://smart.servier.com/?s=nucleosome. SAM: S-adenosyl-L-methione.
resulting in the formation of the H3K27me3 epigenetic mark and subsequent transcriptional repression .
[10]
EZH2/PRC2-facilitated methylation of H3K27 is part of a gene expression regulatory process, and the end
effect of this chain of events is the compaction of chromatin from “open” euchromatin to “closed”
heterochromatin and functional repression of gene expression by preventing the binding of nuclear
transcription factors [Figure 2]. Many of the genes which EZH2 is involved in silencing are effectors of
cellular differentiation . Thus, EZH2 activity is broadly associated with the prevention of terminal
[11]
differentiation and lineage commitment in cells, and maintaining the capacity for self-renewal and a
pluripotent stem cell phenotype in those cells with its high expression . Through its role in gene
[12]
expression regulation, EZH2 is involved in a variety of biological processes, including regulation of cell
cycle, cell differentiation, cell proliferation, division, and senescence.
A recent meta-analysis of 8 studies has shown that mutations in EZH2 confer a poorer prognosis for
patients with myeloid neoplasms, such as acute myeloid leukaemia . Likewise results from a Phase-II trial
[13]
of the EZH2 inhibitor, Tazemetostat, in relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma patients with EZH2