Page 51 - Read Online
P. 51
Pinnamaneni et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2021;7:7 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.94 Page 9 of 14
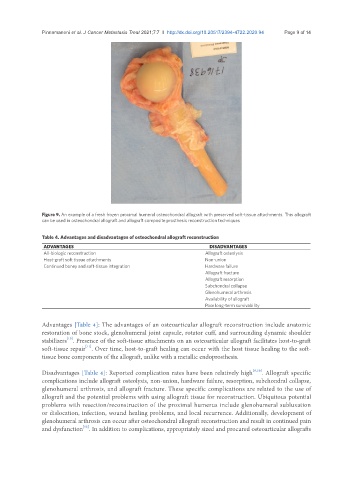
Figure 9. An example of a fresh frozen proximal humeral osteochondral allograft with preserved soft-tissue attachments. This allograft
can be used in osteochondral allograft and allograft composite prosthesis reconstruction techniques
Table 4. Advantages and disadvantages of osteochondral allograft reconstruction
ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES
All-biologic reconstruction Allograft osteolysis
Host-graft soft tissue attachments Non-union
Continued boney and soft-tissue integration Hardware failure
Allograft fracture
Allograft resorption
Subchondral collapse
Glenohumeral arthrosis
Availability of allograft
Poor long-term survivability
Advantages [Table 4]: The advantages of an osteoarticular allograft reconstruction include anatomic
restoration of bone stock, glenohumeral joint capsule, rotator cuff, and surrounding dynamic shoulder
[10]
stabilizers . Presence of the soft-tissue attachments on an osteoarticular allograft facilitates host-to-graft
soft-tissue repair . Over time, host-to-graft healing can occur with the host tissue healing to the soft-
[11]
tissue bone components of the allograft, unlike with a metallic endoprosthesis.
Disadvantages [Table 4]: Reported complication rates have been relatively high [9,10] . Allograft specific
complications include allograft osteolysis, non-union, hardware failure, resorption, subchondral collapse,
glenohumeral arthrosis, and allograft fracture. These specific complications are related to the use of
allograft and the potential problems with using allograft tissue for reconstruction. Ubiquitous potential
problems with resection/reconstruction of the proximal humerus include glenohumeral subluxation
or dislocation, infection, wound healing problems, and local recurrence. Additionally, development of
glenohumeral arthrosis can occur after osteochondral allograft reconstruction and result in continued pain
[12]
and dysfunction . In addition to complications, appropriately sized and procured osteoarticular allografts