Page 61 - Read Online
P. 61
Dave et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:46 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.106 Page 23 of 36
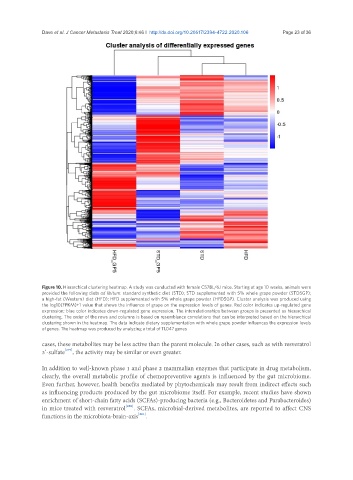
Figure 10. Hierarchical clustering heatmap. A study was conducted with female C57BL/6J mice. Starting at age 10 weeks, animals were
provided the following diets ad libitum: standard synthetic diet (STD); STD supplemented with 5% whole grape powder (STD5GP);
a high-fat (Western) diet (HFD); HFD supplemented with 5% whole grape powder (HFD5GP). Cluster analysis was produced using
the log10(FPKM)+1 value that shows the influence of grape on the expression levels of genes. Red color indicates up-regulated gene
expression; blue color indicates down-regulated gene expression. The interrelationships between groups is presented as hierarchical
clustering. The order of the rows and columns is based on resemblance correlations that can be interpreted based on the hierarchical
clustering shown in the heatmap. The data indicate dietary supplementation with whole grape powder influences the expression levels
of genes. The heatmap was produced by analyzing a total of 11,047 genes
cases, these metabolites may be less active than the parent molecule. In other cases, such as with resveratrol
3’-sulfate [279] , the activity may be similar or even greater.
In addition to well-known phase 1 and phase 2 mammalian enzymes that participate in drug metabolism,
clearly, the overall metabolic profile of chemopreventive agents is influenced by the gut microbiome.
Even further, however, health benefits mediated by phytochemicals may result from indirect effects such
as influencing products produced by the gut microbiome itself. For example, recent studies have shown
enrichment of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)-producing bacteria (e.g., Bacteroidetes and Parabacteroides)
in mice treated with resveratrol [280] . SCFAs, microbial-derived metabolites, are reported to affect CNS
functions in the microbiota-brain-axis [281] .