Page 57 - Read Online
P. 57
Dave et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:46 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.106 Page 19 of 36
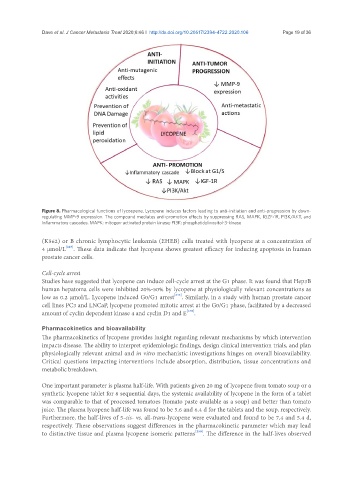
Figure 8. Pharmacological functions of lycoepene. Lycopene induces factors leading to anti-initiation and anti-progression by down-
regulating MMP-9 expression. The compound mediates anti-promotion effects by suppressing RAS, MAPK, IGZF-1R, PI3K/AKT, and
inflammatory cascades. MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase
(K562) or B chronic lymphocytic leukemia (EHEB) cells treated with lycopene at a concentration of
4 µmol/L [249] . These data indicate that lycopene shows greatest efficacy for inducing apoptosis in human
prostate cancer cells.
Cell-cycle arrest
Studies have suggested that lycopene can induce cell-cycle arrest at the G1 phase. It was found that Hep3B
human hepatoma cells were inhibited 20%-50% by lycopene at physiologically relevant concentrations as
low as 0.2 µmol/L. Lycopene induced G0/G1 arrest [246] . Similarly, in a study with human prostate cancer
cell lines PC3 and LNCaP, lycopene promoted mitotic arrest at the G0/G1 phase, facilitated by a decreased
amount of cyclin dependent kinase 4 and cyclin D1 and E [248] .
Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability
The pharmacokinetics of lycopene provides insight regarding relevant mechanisms by which intervention
impacts disease. The ability to interpret epidemiologic findings, design clinical intervention trials, and plan
physiologically relevant animal and in vitro mechanistic investigations hinges on overall bioavailability.
Critical questions impacting interventions include absorption, distribution, tissue concentrations and
metabolic breakdown.
One important parameter is plasma half-life. With patients given 20 mg of lycopene from tomato soup or a
synthetic lycopene tablet for 8 sequential days, the systemic availability of lycopene in the form of a tablet
was comparable to that of processed tomatoes (tomato paste available as a soup) and better than tomato
juice. The plasma lycopene half-life was found to be 5.6 and 6.4 d for the tablets and the soup, respectively.
Furthermore, the half-lives of 5-cis- vs. all-trans-lycopene were evaluated and found to be 7.4 and 5.4 d,
respectively. These observations suggest differences in the pharmacokinetic parameter which may lead
to distinctive tissue and plasma lycopene isomeric patterns [250] . The difference in the half-lives observed