Page 56 - Read Online
P. 56
Page 18 of 36 Dave et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:46 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.106
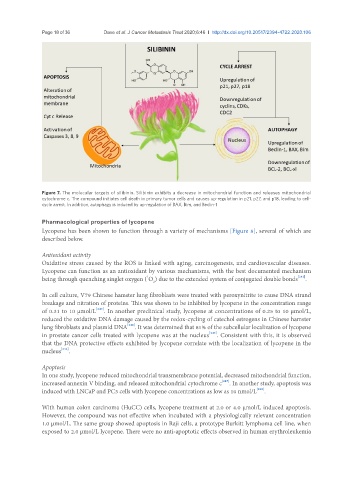
Figure 7. The molecular targets of silibinin. Silibinin exhibits a decrease in mitochondrial function and releases mitochondrial
cytochrome c. The compound initiates cell death in primary tumor cells and causes up-regulation in p21, p27, and p18, leading to cell-
cycle arrest. In addition, autophagy is induced by up-regulation of BAX, Bim, and Beclin-1
Pharmacological properties of lycopene
Lycopene has been shown to function through a variety of mechanisms [Figure 8], several of which are
described below.
Antioxidant activity
Oxidative stress caused by the ROS is linked with aging, carcinogenesis, and cardiovascular diseases.
Lycopene can function as an antioxidant by various mechanisms, with the best documented mechanism
1
being through quenching singlet oxygen ( O ) due to the extended system of conjugated double bonds [242] .
2
In cell culture, V79 Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts were treated with peroxynitrite to cause DNA strand
breakage and nitration of proteins. This was shown to be inhibited by lycopene in the concentration range
of 0.31 to 10 µmol/L [243] . In another preclinical study, lycopene at concentrations of 0.25 to 10 µmol/L,
reduced the oxidative DNA damage caused by the redox-cycling of catechol estrogens in Chinese hamster
lung fibroblasts and plasmid DNA [244] . It was determined that 81% of the subcellular localization of lycopene
in prostate cancer cells treated with lycopene was at the nucleus [245] . Consistent with this, it is observed
that the DNA protective effects exhibited by lycopene correlate with the localization of lycopene in the
nucleus [246] .
Apoptosis
In one study, lycopene reduced mitochondrial transmembrane potential, decreased mitochondrial function,
increased annexin V binding, and released mitochondrial cytochrome c [247] . In another study, apoptosis was
induced with LNCaP and PC3 cells with lycopene concentrations as low as 10 nmol/L [248] .
With human colon carcinoma (HuCC) cells, lycopene treatment at 2.0 or 4.0 µmol/L induced apoptosis.
However, the compound was not effective when incubated with a physiologically relevant concentration
1.0 µmol/L. The same group showed apoptosis in Raji cells, a prototype Burkitt lymphoma cell line, when
exposed to 2.0 µmol/L lycopene. There were no anti-apoptotic effects observed in human erythroleukemia