Page 99 - Read Online
P. 99
Tessari et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:18 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.32 Page 3 of 11
A
B
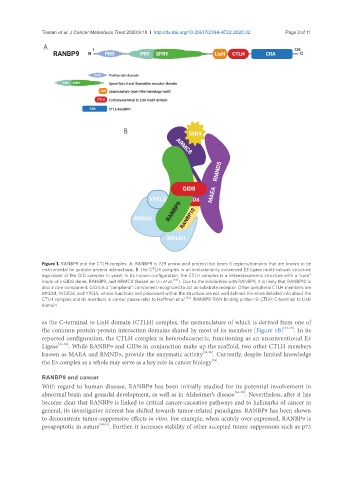
Figure 1. RANBP9 and the CTLH complex. A: RANBP9 is 729 amino acid protein that bears 5 regions/domains that are known to be
instrumental for protein-protein interactions; B: the CTLH complex is an evolutionarily conserved E3 ligase multi-subunit structure
equivalent of the GID complex in yeast. In its known configuration, the CTLH complex is a heterodecameric structure with a “core”
made of a GID8 dimer, RANBP9, and ARMC8 (based on Liu et al. [93] ). Due to the similarities with RANBP9, it is likely that RANBP10 is
also a core component. GID4 is a “peripheral” component recognized to act as substrate receptor. Other peripheral CTLH members are
MKLN1, WDR26, and YPEL5, whose functions and placement within the structure are not well defined. For more detailed info about the
CTLH complex and its members in cancer please refer to Huffman et al. [34] . RANBP9: RAN binding protein 9; CTLH: C-terminal to LisH
domain
as the C-terminal to LisH domain (CTLH) complex, the nomenclature of which is derived from one of
the common protein-protein interaction domains shared by most of its members [Figure 1B] [31-33] . In its
reported configuration, the CTLH complex is heterodecameric, functioning as an unconventional E3
Ligase [31,32] . While RANBP9 and GID8 in conjunction make up the scaffold, two other CTLH members
known as MAEA and RMND5, provide the enzymatic activity [31,32] . Currently, despite limited knowledge
[34]
the E3 complex as a whole may serve as a key role in cancer biology .
RANBP9 and cancer
With regard to human disease, RANBP9 has been initially studied for its potential involvement in
abnormal brain and gonadal development, as well as in Alzheimer’s disease [35-39] . Nevertheless, after it has
become clear that RANBP9 is linked to critical cancer-causative pathways and to hallmarks of cancer in
general, its investigative interest has shifted towards tumor-related paradigms. RANBP9 has been shown
to demonstrate tumor-suppressive effects in vitro. For example, when acutely over-expressed, RANBP9 is
proapoptotic in nature [40,41] . Further, it increases stability of other accepted tumor suppressors such as p73