Page 28 - Read Online
P. 28
Kodama et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2018;4:56 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.61 Page 5 of 11
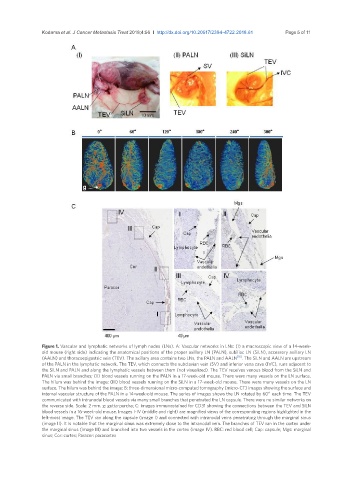
Figure 1. Vascular and lymphatic networks of lymph nodes (LNs). A: Vascular networks in LNs: (I) a macroscopic view of a 14-week-
old mouse (right side) indicating the anatomical positions of the proper axillary LN (PALN), subiliac LN (SiLN), accessory axillary LN
(AALN) and thoracoepigastric vein (TEV). The axillary area contains two LNs, the PALN and AALN [16] . The SiLN and AALN are upstream
of the PALN in the lymphatic network. The TEV, which connects the subclavian vein (SV) and inferior vena cava (IVC), runs adjacent to
the SiLN and PALN and along the lymphatic vessels between them (not visualized). The TEV receives venous blood from the SiLN and
PALN via small branches; (II) blood vessels running on the PALN in a 17-week-old mouse. There were many vessels on the LN surface.
The hilum was behind the image; (III) blood vessels running on the SiLN in a 17-week-old mouse. There were many vessels on the LN
surface. The hilum was behind the image: B: three-dimensional micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) images showing the surface and
internal vascular structure of the PALN in a 14-week-old mouse. The series of images shows the LN rotated by 60º each time. The TEV
communicated with intranodal blood vessels via many small branches that penetrated the LN capsule. There were no similar networks on
the reverse side. Scale: 2 mm. g: gutta-percha; C: images immunostained for CD31 showing the connections between the TEV and SiLN
blood vessels in a 16-week-old mouse. Images I-IV (middle and right) are magnified views of the corresponding regions highlighted in the
left-most image. The TEV ran along the capsule (image I) and connected with intranodal veins penetrating through the marginal sinus
(image II). It is notable that the marginal sinus was extremely close to the intranodal vein. The branches of TEV ran in the cortex under
the marginal sinus (image III) and branched into two vessels in the cortex (image IV). RBC: red blood cell; Cap: capsule; Mgs: marginal
sinus; Cor: cortex; Paracor: paracortex