Page 265 - Read Online
P. 265
Mizejewski. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:35 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.70 Page 7 of 11
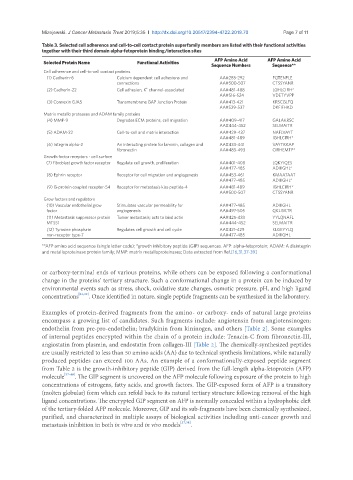
Table 3. Selected cell adherence and cell-to-cell contact protein superfamily members are listed with their functional activities
together with their third domain alpha-fetoprotein binding/interaction sites
Selected Protein Name Functional Activities AFP Amino Acid AFP Amino Acid
Sequence Numbers Sequence**
Cell adherence and cell-to-cell contact proteins
(1) Cadherin-6 Calcium dependent cell adhesions and AA#285-292 FQTENPLE
connections AA#500-507 CTSSYANR
+
(2) Cadherin-22 Cell adhesion, K channel-associated AA#481-488 LGHLCIRH*
AA#516-524 VDETYVPP
(3) Connexin GJA5 Transmembrane GAP Junction Protein AA#413-421 KRSCGLFQ
AA#529-537 DKFIFHKD
Matrix metallo proteases and ADAM family proteins
(4) MMP-9 Degrades ECM proteins, cell migration AA#409-417 GALAKRSC
AA#444-452 SELMAITR
(5) ADAM-22 Cell-to-cell and matrix interaction AA#429-437 NAFLVAYT
AA#481-489 IGHLCIRH*
(6) Integrin alpha-2 An interacting protein for laminin, collagen and AA#433-441 VAYTKKAP
fibronectin AA#485-493 CIRHEMTP*
Growth factor receptors - cell surface
(7) Fibroblast growth factor receptor Regulate cell growth, proliferation AA#401-408 LQKYIQES
AA#477-485 ADIIIGHL*
(8) Ephrin receptor Receptor for cell migration and angiogenesis AA#453-461 KMAATAAT
AA#477-485 ADIIIGHL*
(9) G-protein coupled receptor-54 Receptor for metastasis kiss peptide-4 AA#481-489 IGHLCIRH*
AA#500-507 CTSSYANR
Grow factors and regulators
(10) Vascular endothelial grow Stimulates vascular permeability for AA#477-485 ADIIIGHL
factor angiogenesis AA#497-505 QKLISKTR
(11) Metastasis suppressor protein Tumor metastasis; acts to bind actin AA#425-433 YYLQNAFL
MTSS1 AA#444-452 SELMAITR
(12) Tyrosine phosphate Regulates cell growth and cell cycle AA#421-429 KLGEYYLQ
non-receptor type-7 AA#477-485 ADIIIGHL
**AFP amino acid sequence (single letter code); *growth inhibitory peptide (GIP) sequences. AFP: alpha-fetoprotein; ADAM: A disintegrin
and metalloproteinase protein family; MMP: matrix metalloproteinases; Data extracted from Ref.[16,31,37-39]
or carboxy-terminal ends of various proteins, while others can be exposed following a conformational
change in the proteins’ tertiary structure. Such a conformational change in a protein can be induced by
environmental events such as stress, shock, oxidative state changes, osmotic pressure, pH, and high ligand
concentrations [31,32] . Once identified in nature, single peptide fragments can be synthesized in the laboratory.
Examples of protein-derived fragments from the amino- or carboxy- ends of natural large proteins
encompass a growing list of candidates. Such fragments include: angiotensin from angiotensinogen;
endothelin from pre-pro-endothelin; bradykinin from kininogen, and others [Table 2]. Some examples
of internal peptides encrypted within the chain of a protein include: Tenacin-C from fibronectin-III,
angiostatin from plasmin, and endostatin from collagen-III [Table 2]. The chemically-synthesized peptides
are usually restricted to less than 50 amino acids (AA) due to technical synthesis limitations, while naturally
produced peptides can exceed 100 AAs. An example of a conformationally-exposed peptide segment
from Table 2 is the growth-inhibitory peptide (GIP) derived from the full-length alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)
molecule [37-40] . The GIP segment is uncovered on the AFP molecule following exposure of the protein to high
concentrations of estrogens, fatty acids, and growth factors. The GIP-exposed form of AFP is a transitory
(molten globular) form which can refold back to its natural tertiary structure following removal of the high
ligand concentrations. The encrypted GIP segment on AFP is normally concealed within a hydrophobic cleft
of the tertiary-folded AFP molecule. Moreover, GIP and its sub-fragments have been chemically synthesized,
purified, and characterized in multiple assays of biological activities including anti-cancer growth and
metastasis inhibition in both in vitro and in vivo models [37,38] .