Page 37 - Read Online
P. 37
Kondapuram et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:32 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.105 Page 15 of 25
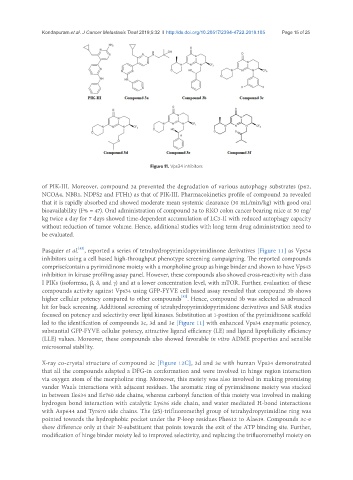
Figure 11. Vps34 inhibitors
of PIK-III. Moreover, compound 3a prevented the degradation of various autophagy substrates (p62,
NCOA4, NBR1, NDPS2 and FTH1) as that of PIK-III. Pharmacokinetics profile of compound 3a revealed
that it is rapidly absorbed and showed moderate mean systemic clearance (30 mL/min/kg) with good oral
bioavailability (F% = 47). Oral administration of compound 3a to RKO colon cancer bearing mice at 50 mg/
kg twice a day for 7 days showed time-dependent accumulation of LC3-II with reduced autophagy capacity
without reduction of tumor volume. Hence, additional studies with long term drug administration need to
be evaluated.
[82]
Pasquier et al. , reported a series of tetrahydropyrimidopyrimidinone derivatives [Figure 11] as Vps34
inhibitors using a cell based high-throughput phenotype screening campaigning. The reported compounds
comprise/contain a pyrimidinone moiety with a morpholine group as hinge binder and shown to have Vps43
inhibition in kinase profiling assay panel. However, these compounds also showed cross-reactivity with class
I PIKs (isoformsα, β, δ, and γ) and at a lower concentration level, with mTOR. Further, evaluation of these
compounds activity against Vps34 using GFP-FYVE cell based assay revealed that compound 3b shows
[82]
higher cellular potency compared to other compounds . Hence, compound 3b was selected as advanced
hit for back screening. Additional screening of tetrahydropyrimidopyrimidone derivatives and SAR studies
focused on potency and selectivity over lipid kinases. Substitution at 1-position of the pyrimidinone scaffold
led to the identification of compounds 3c, 3d and 3e [Figure 11] with enhanced Vps34 enzymatic potency,
substantial GFP-FYVE cellular potency, attractive ligand efficiency (LE) and ligand lipophilicity efficiency
(LLE) values. Moreover, these compounds also showed favorable in vitro ADME properties and sensible
microsomal stability.
X-ray co-crystal structure of compound 3c [Figure 12C], 3d and 3e with human Vps34 demonstrated
that all the compounds adapted a DFG-in conformation and were involved in hinge region interaction
via oxygen atom of the morpholine ring. Moreover, this moiety was also involved in making promising
vander Waals interactions with adjacent residues. The aromatic ring of pyrimidinone moiety was stacked
in between Ile634 and Ile760 side chains, whereas carbonyl function of this moiety was involved in making
hydrogen bond interaction with catalytic Ly636 side chain, and water mediated H-bond interactions
with Asp644 and Tyr670 side chains. The (2S)-trifluoromethyl group of tetrahydropyrimidine ring was
pointed towards the hydrophobic pocket under the P-loop residues Phe612 to Ala619. Compounds 3c-e
show difference only at their N-substituent that points towards the exit of the ATP binding site. Further,
modification of hinge binder moiety led to improved selectivity, and replacing the trifluoromethyl moiety on