Page 42 - Read Online
P. 42
Page 20 of 25 Kondapuram et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:32 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.105
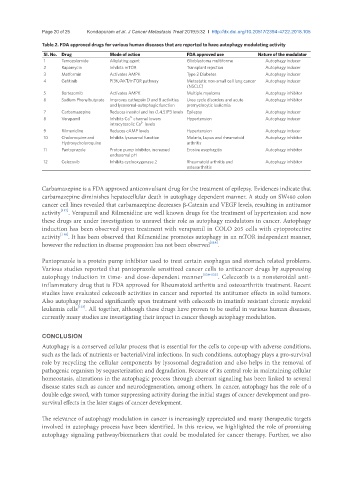
Table 2. FDA approved drugs for various human diseases that are reported to have autophagy modulating activity
SI. No. Drug Mode of action FDA approved use Nature of the modulator
1 Temozolomide Alkylating agent Glioblastoma multiforme Autophagy inducer
2 Rapamycin Inhibits mTOR Transplant rejection Autophagy inducer
3 Metformin Activates AMPK Type 2 Diabetes Autophagy inducer
4 Gefitinib PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer Autophagy inducer
(NSCLC)
5 Bortezomib Activates AMPK Multiple myeloma Autophagy inhibitor
6 Sodium Phenylbutyrate Improves cathepsin D and B activities Urea cycle disorders and acute Autophagy inhibitor
and lysosomal-autophagic function promyelocytic leukemia
7 Carbamazepine Reduces inositol and Ins (1,4,5)P3 levels Epilepsy Autophagy inducer
2+
8 Verapamil Inhibits Ca channel lowers Hypertension Autophagy inducer
2+
intracytosolic Ca levels
9 Rilmenidine Reduces cAMP levels Hypertension Autophagy inducer
10 Choloroquine and Inhibits lysosomal function Malaria, Lupus and rheumatoid Autophagy inhibitor
Hydroxycholoroquine arthritis
11 Pantoprazole Proton pump inhibitor, increased Erosive esophagitis Autophagy inhibitor
endosomal pH
12 Celecoxib Inhibits cyclooxygenase 2 Rheumatoid arthritis and Autophagy inhibitor
osteoarthritis
Carbamazepine is a FDA approved anticonvulsant drug for the treatment of epilepsy. Evidences indicate that
carbamazepine diminishes hepatocellular death in autophagy dependent manner. A study on SW480 colon
cancer cell lines revealed that carbamazepine decreases β-Catenin and VEGF levels, resulting in antitumor
activity [117] . Verapamil and Rilmenidine are well known drugs for the treatment of hypertension and now
these drugs are under investigation to unravel their role as autophagy modulators in cancer. Autophagy
induction has been observed upon treatment with verapamil in COLO 205 cells with cytoprotective
activity [118] . It has been observed that Rilmenidine promotes autophagy in an mTOR independent manner,
however the reduction in disease progression has not been observed [119] .
Pantoprazole is a protein pump inhibitor used to treat certain esophagus and stomach related problems.
Various studies reported that pantoprazole sensitized cancer cells to anticancer drugs by suppressing
autophagy induction in time- and dose-dependent manner [120-122] . Celecoxib is a nonsteroidal anti-
inflammatory drug that is FDA approved for Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis treatment. Recent
studies have evaluated celecoxib activities in cancer and reported its antitumor effects in solid tumors.
Also autophagy reduced significantly upon treatment with celecoxib in imatinib resistant chronic myeloid
leukemia cells [123] . All together, although these drugs have proven to be useful in various human diseases,
currently many studies are investigating their impact in cancer though autophagy modulation.
CONCLUSION
Autophagy is a conserved cellular process that is essential for the cells to cope-up with adverse conditions,
such as the lack of nutrients or bacterial/viral infections. In such conditions, autophagy plays a pro-survival
role by recycling the cellular components by lysosomal degradation and also helps in the removal of
pathogenic organism by sequesterization and degradation. Because of its central role in maintaining cellular
homeostasis, alterations in the autophagic process through aberrant signaling has been linked to several
disease states such as cancer and neurodegeneration, among others. In cancer, autophagy has the role of a
double edge sword, with tumor suppressing activity during the initial stages of cancer development and pro-
survival effects in the later stages of cancer development.
The relevance of autophagy modulation in cancer is increasingly appreciated and many therapeutic targets
involved in autophagy process have been identified. In this review, we highlighted the role of promising
autophagy signaling pathway/biomarkers that could be modulated for cancer therapy. Further, we also