Page 91 - Read Online
P. 91
Othman et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2018;4:50 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.41 Page 5 of 9
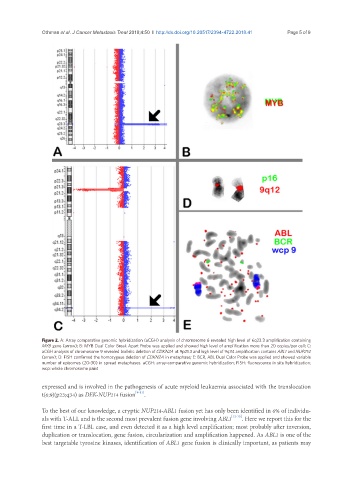
Figure 2. A: Array comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH) analysis of chromosome 6 revealed high level of 6q23.3 amplification containing
MYB gene (arrow); B: MYB Dual Color Break Apart Probe was applied and showed high level of amplification more than 20 copies/per cell; C:
aCGH analysis of chromosome 9 revealed biallelic deletion of CDKN2A at 9p21.3 and high level of 9q34 amplification contains ABL1 and NUP214
(arrow); D: FISH confirmed the homozygous deletion of CDKN2A in metaphase; E: BCR, ABL Dual Color Probe was applied and showed variable
number of episomes (20-30) in spread metaphases. aCGH: array-comparative genomic hybridization; FISH: fluorescence in situ hybridization;
wcp: whole chromosome paint
expressed and is involved in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukaemia associated with the translocation
t(6;9)(p23;q34) as DEK-NUP214 fusion [9-11] .
To the best of our knowledge, a cryptic NUP214-ABL1 fusion yet has only been identified in 6% of individu-
als with T-ALL and is the second most prevalent fusion gene involving ABL1 [12-15] . Here we report this for the
first time in a T-LBL case, and even detected it as a high level amplification; most probably after inversion,
duplication or translocation, gene fusion, circularization and amplification happened. As ABL1 is one of the
best targetable tyrosine kinases, identification of ABL1 gene fusion is clinically important, as patients may