Page 40 - Read Online
P. 40
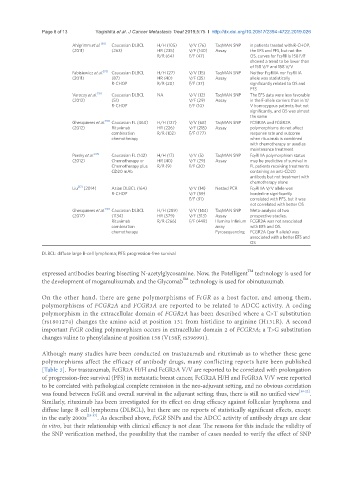
Page 6 of 13 Yagishita et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:75 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.026
Ahlgrimm et al. [30] Caucasian DLBCL H/H (105) V/V (76) TaqMAN SNP in patients treated with R-CHOP,
(2011) (263) HR (235) V/F (140) Assay the EFS and PFS, but not the
R/R (64) F/F (47) OS, curves for FcgRIIIa 158 F/F
showed a trend to be lower than
of 158 V/F and 158 V/V
Fabisiewicz et al. [31] Caucasian DLBCL H/H (27) V/V (15) TaqMAN SNP Neither FcgRIIA nor FcgRIIIA
(2011) (87) HR (40) V/F (35) Assay allele was statistically
R-CHOP R/R (20) F/F (37) significantly related to OS and
PFS
Varoczy et al. [35] Caucasian DLBCL NA V/V (12) TaqMAN SNP The EFS data were less favorable
(2012) (51) V/F (29) Assay in the F-allele carriers than in V/
R-CHOP F/F (10) V homozygous patients, but not
significantly, and OS was almost
the same
Ghesquieres et al. [33] Caucasian FL (460) H/H (127) V/V (68) TaqMAN SNP FCGR3A and FCGR2A
(2012) Rituximab HR (226) V/F (215) Assay polymorphisms do not affect
combination R/R (102) F/F (177) response rate and outcome
chemotherapy when rituximab is combined
with chemotherapy or used as
maintenance treatment
Persky et al. [34] Caucasian FL (142) H/H (17) V/V (5) TaqMAN SNP FcgRIIIA polymorphism status
(2012) Chemotherapy or HR (40) V/F (29) Assay may be predictive of survival in
Chemotherapy plus R/R (9) F/F (20) FL patients receiving treatments
CD20 mAb containing an anti-CD20
antibody but not treatment with
chemotherapy alone
Liu [37] (2014) Asian DLBCL (164) V/V (14) Nested PCR FcgRIIIA V/V allele was
R-CHOP V/F (59) borderline significantly
F/F (91) correlated with PFS, but it was
not correlated with better OS
Ghesquieres et al. [36] Caucasian DLBCL H/H (289) V/V (144) TaqMAN SNP Meta-analysis of two
(2017) (1134) HR (579) V/F (513) Assay prospective studies.
Rituximab R/R (266) F/F (449) Illumina Infinium FCGR3A was not associated
combination array with EFS and OS.
chemotherapy Pyrosequencing FCGR2A (per R allele) was
associated with a better EFS and
OS
DLBCL: diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; PFS: progression-free survival
TM
expressed antibodies bearing bisecting N-acetylglycosamine. Now, the Potelligent technology is used for
TM
the development of mogamulizumab, and the Glycomab technology is used for obinutuzumab.
On the other hand, there are gene polymorphisms of FcGR as a host factor, and among them,
polymorphisms of FCGR2A and FCGR3A are reported to be related to ADCC activity. A coding
polymorphism in the extracellular domain of FCGR2A has been described where a C>T substitution
(rs1801274) changes the amino acid at position 131 from histidine to arginine (H131R). A second
important FcGR coding polymorphism occurs in extracellular domain 2 of FCGR3A; a T>G substitution
changes valine to phenylalanine at position 158 (V158F, rs396991).
Although many studies have been conducted on trastuzumab and rituximab as to whether these gene
polymorphisms affect the efficacy of antibody drugs, many conflicting reports have been published
[Table 3]. For trastuzumab, FcGR2A H/H and FcGR3A V/V are reported to be correlated with prolongation
of progression-free survival (PFS) in metastatic breast cancer, FcGR2A H/H and FcGR3A V/V were reported
to be correlated with pathological complete remission in the neo-adjuvant setting, and no obvious correlation
was found between FcGR and overall survival in the adjuvant setting; thus, there is still no unified view [19-22] .
Similarly, rituximab has been investigated for its effect on drug efficacy against follicular lymphoma and
diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), but there are no reports of statistically significant effects, except
in the early 2000s [23-37] . As described above, FcGR SNPs and the ADCC activity of antibody drugs are clear
in vitro, but their relationship with clinical efficacy is not clear. The reasons for this include the validity of
the SNP verification method, the possibility that the number of cases needed to verify the effect of SNP