Page 193 - Read Online
P. 193
Page 4 of 9 Tokunaga et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2018;4:40 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2017.80
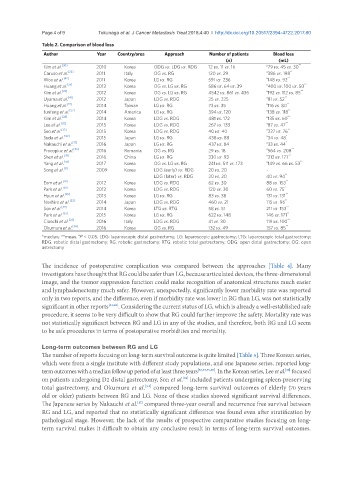
Table 2. Comparison of blood loss
Author Year Country/area Approach Number of patients Blood loss
(n) (mL)
Kim et al. [30] 2010 Korea ODG vs. LDG vs. RDG 12 vs. 11 vs. 16 a 79 vs. 45 vs. 30 **
Caruso et al. [22] 2011 Italy OG vs. RG 120 vs. 29 a 386 vs. 198 **
Woo et al. [42] 2011 Korea LG vs. RG 591 vs. 236 a 148 vs. 92 **
Huang et al. [25] 2012 Korea OG vs. LG vs. RG 586 vs. 64 vs. 39 a 400 vs. 100 vs. 50 **
Kim et al. [29] 2012 Korea OG vs. LG vs. RG 4542 vs. 861 vs. 436 a 192 vs. 112 vs. 85 **
Uyama et al. [41] 2012 Japan LDG vs. RDG 25 vs. 225 a 81 vs. 52 **
Huang et al. [19] 2014 Taiwan LG vs. RG 73 vs. 35 a 116 vs. 80 **
Junfeng et al. [27] 2014 America LG vs. RG 394 vs. 120 a 138 vs. 118 **
Kim et al. [28] 2014 Korea LDG vs. RDG 481 vs. 172 a 135 vs. 60 **
Lee et al. [32] 2015 Korea LDG vs. RDG 267 vs. 133 a 87 vs. 47 **
Seo et al. [37] 2015 Korea LDG vs. RDG 40 vs. 40 a 227 vs. 76 **
Suda et al. [40] 2015 Japan LG vs. RG 438 vs. 88 a 34 vs. 48 *
Nakauchi et al. [17] 2016 Japan LG vs. RG 437 vs. 84 a 33 vs. 44 *
Procopiuc et al. [36] 2016 Romania OG vs. RG 29 vs. 18 a 564 vs. 208 **
Shen et al. [38] 2016 China LG vs. RG 330 vs. 93 a 213 vs. 177 **
Yang et al. [43] 2017 Korea OG vs. LG vs. RG 241 vs. 511 vs. 173 a 149 vs. 66 vs. 53 **
Song et al. [9] 2009 Korea LDG (early) vs. RDG 20 vs. 20 -
LDG (later) vs. RDG 20 vs. 20 40 vs. 94 **
Eom et al. [18] 2012 Korea LDG vs. RDG 62 vs. 30 88 vs. 153 **
Park et al. [20] 2012 Korea LDG vs. RDG 120 vs. 30 60 vs. 75 *
Hyun et al. [26] 2013 Korea LG vs. RG 83 vs. 38 131 vs. 131 **
Noshiro et al. [33] 2014 Japan LDG vs. RDG 460 vs. 21 115 vs. 96 **
Son et al. [39] 2014 Korea LTG vs. RTG 58 vs. 51 211 vs. 153 **
Park et al. [35] 2015 Korea LG vs. RG 622 vs. 148 146 vs. 171 **
Cianchi et al. [23] 2016 Italy LDG vs. RDG 41 vs. 30 119 vs. 100 **
Okumura et al. [34] 2016 Korea OG vs. RG 132 vs. 49 157 vs. 85 **
a
*median; **mean. P < 0.05. LDG: laparoscopic distal gastrectomy; LG: laparoscopic gastrectomy; LTG: laparoscopic total gastrectomy;
RDG: robotic distal gastrectomy; RG: robotic gastrectomy; RTG: robotic total gastrectomy; ODG: open distal gastrectomy; OG: open
astrectomy
The incidence of postoperative complication was compared between the approaches [Table 4]. Many
investigators have thought that RG could be safer than LG, because articulated devices, the three-dimensional
image, and the tremor suppression function could make recognition of anatomical structures much easier
and lymphadenectomy much safer. However, unexpectedly, significantly lower morbidity rate was reported
only in two reports, and the difference, even if morbidity rate was lower in RG than LG, was not statistically
significant in other reports [33,41] . Considering the current status of LG, which is already a well-established safe
procedure, it seems to be very difficult to show that RG could further improve the safety. Mortality rate was
not statistically significant between RG and LG in any of the studies, and therefore, both RG and LG seem
to be safe procedures in terms of postoperative morbidities and mortality.
Long-term outcomes between RG and LG
The number of reports focusing on long-term survival outcome is quite limited [Table 5]. Three Korean series,
which were from a single institute with different study populations, and one Japanese series, reported long-
term outcomes with a median follow up period of at least three years [32,33,35,40] . In the Korean series, Lee et al. focused
[32]
on patients undergoing D2 distal gastrectomy, Son et al. included patients undergoing spleen-preserving
[39]
total gastrectomy, and Okumura et al. compared long-term survival outcomes of elderly (70 years
[34]
old or older) patients between RG and LG. None of these studies showed significant survival differences.
The Japanese series by Nakauchi et al. compared three-year overall and recurrence free survival between
[17]
RG and LG, and reported that no statistically significant difference was found even after stratification by
pathological stage. However, the lack of the results of prospective comparative studies focusing on long-
term survival makes it difficult to obtain any conclusive result in terms of long-term survival outcomes.