Page 9 - Read Online
P. 9
Calais da Silva et al. Systemic humoral responses during BCG treatment
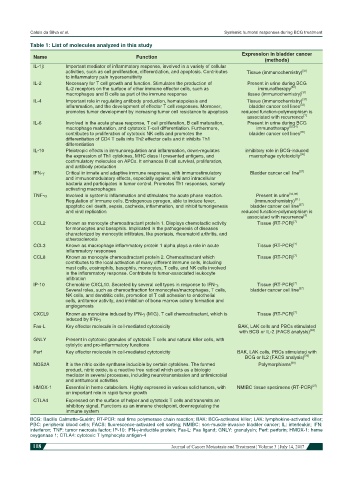
Table 1: List of molecules analyzed in this study
Expression in bladder cancer
Name Function
(methods)
IL-1β Important mediator of inflammatory response, involved in a variety of cellular
activities, such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Contributes Tissue (immunochemistry) [31]
to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity
IL-2 Necessary for T cell growth and function. Stimulates the production of Present in urine during BCG
IL-2 receptors on the surface of other immune effector cells, such as immunotherapy [32]
macrophages and B cells as part of the immune response tissue (immunochemistry) [31]
IL-4 Important role in regulating antibody production, hematopoiesis and Tissue (immunochemistry) [31]
inflammation, and the development of effector T cell responses. Moreover, bladder cancer cell lines [33]
promotes tumor development by increasing tumor cell resistance to apoptosis reduced function-polymorphism is
associated with recurrence [7]
IL-6 Involved in the acute phase response, T cell proliferation, B cell maturation, Present in urine during BCG
macrophage maturation, and cytotoxic T-cell differentiation. Furthermore, immunotherapy [32,34]
contributes to proliferation of cytotoxic NK cells and promotes the bladder cancer cell lines [35]
differentiation of CD4 T cells into Th2 effector cells and it inhibits Th1
differentiation
IL-10 Pleiotropic effects in immunoregulation and inflammation, down-regulates inhibitory role in BCG-induced
the expression of Th1 cytokines, MHC class II presented antigens, and macrophage cytotoxicity [36]
costimulatory molecules on APCs. It enhances B cell survival, proliferation,
and antibody production
IFN-γ Critical in innate and adaptive immune responses, with immunostimulatory Bladder cancer cell line [37]
and immunomodulatory effects, especially against viral and intracellular
bacteria and participates in tumor control. Promotes Th1 responses, namely
activating macrophages
TNF-α Involved in systemic inflammation and stimulates the acute phase reaction. Present in urine [32,38]
Regulation of immune cells. Endogenous pyrogen, able to induce fever, (immunochemistry) [31]
apoptotic cell death, sepsis, cachexia, inflammation, and inhibit tumorigenesis bladder cancer cell line [37]
and viral replication reduced function-polymorphism is
associated with recurrence [4]
CCL2 Known as monocyte chemoattractant protein 1. Displays chemotactic activity Tissue (RT-PCR) [7]
for monocytes and basophils. Implicated in the pathogenesis of diseases
characterized by monocytic infiltrates, like psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and
atherosclerosis
CCL3 Known as macrophage inflammatory protein 1 alpha plays a role in acute Tissue (RT-PCR) [7]
inflammatory responses
CCL8 Known as monocyte chemoattractant protein 2. Chemoattractant which Tissue (RT-PCR) [7]
contributes to the local activation of many different immune cells, including
mast cells, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, T cells, and NK cells involved
in the inflammatory response. Contribute to tumor-associated leukocyte
infiltration
IP-10 Chemokine CXCL10. Secreted by several cell types in response to IFN-γ. Tissue (RT-PCR) [7]
Several roles, such as chemoattraction for monocytes/macrophages, T cells, bladder cancer cell line [37]
NK cells, and dendritic cells, promotion of T cell adhesion to endothelial
cells, antitumor activity, and inhibition of bone marrow colony formation and
angiogenesis
CXCL9 Known as monokine induced by IFN-γ (MIG). T cell chemoattractant, which is Tissue (RT-PCR) [7]
induced by IFN-γ
Fas-L Key effector molecule in cell-mediated cytotoxicity BAK, LAK cells and PBCs stimulated
with BCG or IL-2 (FACS analysis) [28]
GNLY Present in cytotoxic granules of cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells, with
cytolytic and pro-inflammatory functions
Perf Key effector molecule in cell-mediated cytotoxicity BAK, LAK cells, PBCs stimulated with
BCG or IL2 (FACS analysis) [28]
NOS2A It is the nitric oxide synthase inducible by certain cytokines. The formed Polymorphisms [39]
product, nitric oxide, is a reactive free radical which acts as a biologic
mediator in several processes, including neurotransmission and antimicrobial
and antitumoral activities
HMOX-1 Essential in heme catabolism. Highly expressed in various solid tumors, with NMIBC tissue specimens (RT-PCR) [27]
an important role in rapid tumor growth
CTLA4 Expressed on the surface of helper and cytotoxic T cells and transmits an
inhibitory signal. Functions as an immune checkpoint, downregulating the
immune system
BCG: Bacille Calmette-Guérin; RT-PCR: real time polymerase chain reaction; BAK: BCG-activated killer; LAK: lymphokine-activated killer;
PBC: peripheral blood cells; FACS: fluorescence-activated cell sorting; NMIBC: non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer; IL: interleukin; IFN:
interferon; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; IP-10: IFN-γ-inducible protein; Fas-L: Fas ligand; GNLY: granulysin; Perf: perforin; HMOX-1: heme
oxygenase 1; CTLA4: cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4
118 Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 3 ¦ July 14, 2017