Page 54 - Read Online
P. 54
Yagawa et al. Cancer immunity and hyperthermia
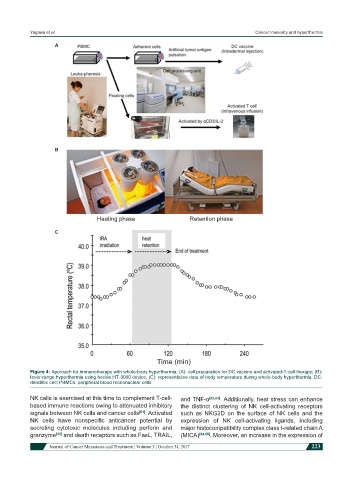
A
B
Heating phase Retention phase
C
Time (min)
Figure 4: Approach for immunotherapy with whole-body hyperthermia. (A): cell preparation for DC vaccine and activated-T-cell therapy; (B):
fever-range hyperthermia using heckle HT-3000 device; (C): representative data of body temperature during whole-body hyperthermia. DC:
dendritic cell; PBMCs: peripheral blood mononuclear cells
NK cells is exercised at this time to complement T-cell- and TNF-α [62,63] . Additionally, heat stress can enhance
based immune reactions owing to attenuated inhibitory the distinct clustering of NK cell-activating receptors
signals between NK cells and cancer cells [61] . Activated such as NKG2D on the surface of NK cells and the
NK cells have nonspecific anticancer potential by expression of NK cell-activating ligands, including
secreting cytotoxic molecules including perforin and major histocompatibility complex class I-related chain A
granzyme [33] and death receptors such as FasL, TRAIL, (MICA) [64,65] . Moreover, an increase in the expression of
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 3 ¦ October 31, 2017 223