Page 53 - Read Online
P. 53
Warawdekar et al. CTCs from patients with metastatic breast cancer
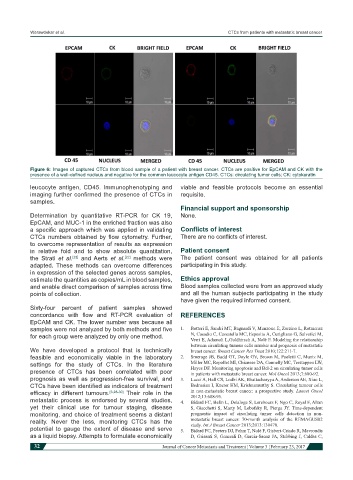
Figure 6: Images of captured CTCs from blood sample of a patient with breast cancer. CTCs are positive for EpCAM and CK with the
presence of a well-defined nucleus and negative for the common leucocyte antigen CD45. CTCs: circulating tumor cells; CK: cytokeratin
leucocyte antigen, CD45. Immunophenotyping and viable and feasible protocols become an essential
imaging further confirmed the presence of CTCs in requisite.
samples.
Financial support and sponsorship
Determination by quantitative RT-PCR for CK 19, None.
EpCAM, and MUC-1 in the enriched fraction was also
a specific approach which was applied in validating Conflicts of interest
CTCs numbers obtained by flow cytometry. Further, There are no conflicts of interest.
to overcome representation of results as expression
in relative fold and to show absolute quantitation, Patient consent
the Strati et al. and Aerts et al. methods were The patient consent was obtained for all patients
[23]
[22]
adapted. These methods can overcome differences participating in this study.
in expression of the selected genes across samples,
estimate the quantities as copies/mL in blood samples, Ethics approval
and enable direct comparison of samples across time Blood samples collected were from an approved study
points of collection. and all the human subjects participating in the study
have given the required informed consent.
Sixty-four percent of patient samples showed
concordance with flow and RT-PCR evaluation of REFERENCES
EpCAM and CK. The lower number was because all
samples were not analyzed by both methods and five 1. Botteri E, Sandri MT, Bagnardi V, Munzone E, Zorzino L, Rotmensz
for each group were analyzed by only one method. N, Casadio C, Cassatella MC, Esposito A, Curigliano G, Salvatici M,
Verri E, Adamoli L,Goldhirsch A, Nolè F. Modeling the relationship
between circulating tumour cells number and prognosis of metastatic
We have developed a protocol that is technically breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2010;122:211-7.
feasible and economically viable in the laboratory 2. Smerage JB, Budd GT, Doyle GV, Brown M, Paoletti C, Muniz M,
settings for the study of CTCs. In the literature Miller MC, Repollet MI, Chianese DA, Connelly MC, Terstappen LW,
Hayes DF. Monitoring apoptosis and Bcl-2 on circulating tumor cells
presence of CTCs has been correlated with poor in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Mol Oncol 2013;7:680-92.
prognosis as well as progression-free survival, and 3. Lucci A, Hall CS, Lodhi AK, Bhattacharyya A, Anderson AE, Xiao L,
CTCs have been identified as indicators of treatment Bedrosian I, Kuerer HM, Krishnamurthy S. Circulating tumour cells
efficacy in different tumours. [6,28-30] Their role in the in non-metastatic breast cancer: a prospective study. Lancet Oncol
2012;13:688-95.
metastatic process is endorsed by several studies, 4. Bidard FC, Belin L, Delaloge S, Lerebours F, Ngo C, Reyal F, Alran
yet their clinical use for tumour staging, disease S, Giacchetti S, Marty M, Lebofsky R, Pierga JY. Time-dependent
monitoring, and choice of treatment seems a distant prognostic impact of circulating tumor cells detection in non-
reality. Never the less, monitoring CTCs has the metastatic breast cancer: 70-month analysis of the REMAGUS02
study. Int J Breast Cancer 2013;2013:130470.
potential to gauge the extent of disease and serve 5. Bidard FC, Peeters DJ, Fehm T, Nolé F, Gisbert-Criado R, Mavroudis
as a liquid biopsy. Attempts to formulate economically D, Grisanti S, Generali D, Garcia-Saenz JA, Stebbing J, Caldas C,
32 Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 3 ¦ February 23, 2017