Page 32 - Read Online
P. 32
Sawabata et al. Circulating tumor cells after lung-cancer biopsy
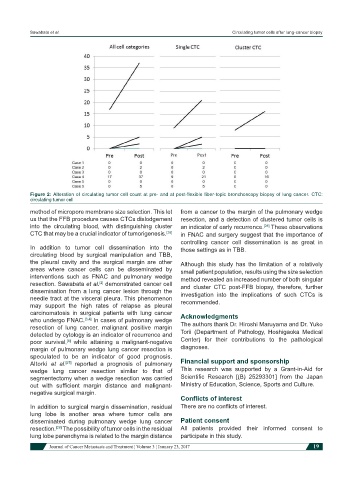
Figure 2: Alteration of circulating tumor cell count at pre- and at post-flexible fiber-topic bronchoscopy biopsy of lung cancer. CTC:
circulating tumor cell
method of micropore membrane size selection. This let from a cancer to the margin of the pulmonary wedge
us that the FFB procedure causes CTCs dislodgement resection, and a detection of clustered tumor cells is
into the circulating blood, with distinguishing cluster an indicator of early recurrence. These observations
[28]
CTC that may be a crucial indicator of tumorigenesis. [26] in FNAC and surgery suggest that the importance of
controlling cancer cell dissemination is as great in
In addition to tumor cell dissemination into the those settings as in TBB.
circulating blood by surgical manipulation and TBB,
the pleural cavity and the surgical margin are other Although this study has the limitation of a relatively
areas where cancer cells can be disseminated by small patient population, results using the size selection
interventions such as FNAC and pulmonary wedge method revealed an increased number of both singular
resection. Sawabata et al. demonstrated cancer cell and cluster CTC post-FFB biopsy, therefore, further
[2]
dissemination from a lung cancer lesion through the investigation into the implications of such CTCs is
needle tract at the visceral pleura. This phenomenon recommended.
may support the high rates of relapse as pleural
carcinomatosis in surgical patients with lung cancer Acknowledgments
who undergo FNAC. [3,4] In cases of pulmonary wedge
resection of lung cancer, malignant positive margin The authors thank Dr. Hiroshi Maruyama and Dr. Yuko
detected by cytology is an indicator of recurrence and Torii (Department of Pathology, Hoshigaoka Medical
poor survival, while attaining a malignant-negative Center) for their contributions to the pathological
[6]
margin of pulmonary wedge lung cancer resection is diagnoses.
speculated to be an indicator of good prognosis.
[27]
Altorki et al. reported a prognosis of pulmonary Financial support and sponsorship
wedge lung cancer resection similar to that of This research was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for
segmentectomy when a wedge resection was carried Scientific Research [(B) 25293301] from the Japan
out with sufficient margin distance and malignant- Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture.
negative surgical margin.
Conflicts of interest
In addition to surgical margin dissemination, residual There are no conflicts of interest.
lung lobe is another area where tumor cells are
disseminated during pulmonary wedge lung cancer Patient consent
resection. The possibility of tumor cells in the residual All patients provided their informed consent to
[28]
lung lobe parenchyma is related to the margin distance participate in this study.
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 3 ¦ January 23, 2017 19