Page 31 - Read Online
P. 31
Sawabata et al. Circulating tumor cells after lung-cancer biopsy
cell was detected at pre-FFB, while in three cases cells the peripheral circulating blood, as can occur with a
were detected at post-FFB (50.0%); no tumor cell was surgical procedure. [12-15]
detected at pre-FFB while some CTCs were detected
at post-FFB in two cases (33.3%) while some CTCs Initially, tumor cell dislodgement to the peripheral
were detected at pre-FFB. Numerous CTCs were circulating blood by surgical manipulation was
detected at post-FFB in one case (17.7%). In addition, demonstrated using a cytological technique, but the
[17]
in the analysis of cluster CTC alone (n = 6), no tumor sensitivity was very low. Later, polymerase chain
cells were detected at pre-FFB and at post-FFB in five reaction [18,19] and flow-cytometry [20] methods were
cases (63.3%), with some CTCs being detected at pre- introduced to improve sensitivity and specificity, but
FFB and many CTCs detected at post-FFB in one case results were not predictable. Morphological detection
(17.7%). The alterations of CTC counts are graphically of CTC dislodgement was shown using the EpCAM
®
demonstrated in Figure 2. positive selection method [CellSearch system
(Janssen Diagnostics, Raritan, NJ)], but the sensitivity
[15]
DISCUSSION was still low. As such, isolated tumor cells (ITC),
surrogates of CTC, were extracted from pulmonary
In our assessment of CTCs at pre-FFB and at post- vein blood, revealing that detecting ITC/CTC was
FFB biopsy, the amount of CTC is not decreased an indicator of early recurrence; the presence of
after an FFB procedure, and in cases involving CTCs cluster ITC/CTC indicated wrong prognosis, using
[21]
the count of CTCs increased at post-FFB. These the EpCAM positive selection method or the CD45
®
results suggest that a tumor biopsy of a lung cancer negativedepression gravity method [RosettSep
[22-24]
lesion has the potential to dislodge tumor cells into (Stemcell Technologies, Vancouver, Canada)]. As
the sensitivity of such CTC detecting methods was
not greater, the sample used pulmonary vein blood,
because it contains more ITC/CTC than the peripheral
circulating blood. [24]
Size selection methods [ISET (Rarecells Diagnostics,
®
Paris, France) and ScreenCell Cyto] are highly
®
sensitive for cluster CTC, and therefore the sampling
of CTC extraction using size selection methods can
use peripheral blood. [16,25] Recently, CTC dislodgement
during surgery for lung cancer was proven by detecting
CTCs in the peripheral circulating blood using a size
selection method, and the presence of cluster CTC has
been an indicator of early recurrence among surgical
lung cancer patients. [13]
A CTC assessment during FFB procedures needs a
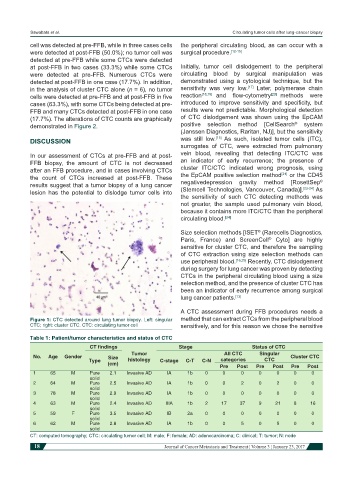
Figure 1: CTC detected around lung tumor biopsy. Left: singular method that can extract CTCs from the peripheral blood
CTC; right: cluster CTC. CTC: circulating tumor cell sensitively, and for this reason we chose the sensitive
Table 1: Patient/tumor characteristics and status of CTC
CT findings Stage Status of CTC
Tumor All CTC Singular
No. Age Gender Size Cluster CTC
Type histology C-stage C-T C-N categories CTC
(cm) Pre Post Pre Post Pre Post
1 65 M Pure 2.1 Invasive AD IA 1b 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
solid
2 64 M Pure 2.5 Invasive AD IA 1b 0 0 2 0 2 0 0
solid
3 78 M Pure 2.9 Invasive AD IA 1b 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
solid
4 63 M Pure 2.4 Invasive AD IIIA 1b 2 17 37 9 21 8 16
solid
5 59 F Pure 3.5 Invasive AD IB 2a 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
solid
6 62 M Pure 2.8 Invasive AD IA 1b 0 0 5 0 5 0 0
solid
CT: computed tomography; CTC: circulating tumor cell; M: male; F: female; AD: adenocarcinoma; C: clinical; T: tumor; N: node
18 Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 3 ¦ January 23, 2017