Page 22 - Read Online
P. 22
Page 215 Zhu et al. Intell Robot 2022;2(3):200222 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2022.13
Table 4 Algorithms for UUV trajectory tracking
Algorithms Logic Benefits Drawbacks
(1) Unsatisfactory
(1) Easy to implement for adaptiveness
Backstepping control [84–88] Design control function by generating the sub- nonlinear system (2) Produce excessive speed
system established based on the Lyapunouv (2) Real-time reaction references and actuator
theorem saturation problems
(1) Suppose a sliding surface mode to follow the
desired tracking (1) Simple algorithm;
Sliding mode control [89–95] Chattering issue
(2) Keep the controlled outputs on the (2) Robust.
surface.
(1) Resolve the online optimization problem in
each timeslot and derive in-time predictions with
minimum errors
(2) Optimization algorithm embedded in the (1) High
control system accuracy not needed
Model predictive system gives an optimized sequence within the (2) In-time reaction Long time consumption
control [96–99,112] due to the recursive com-
pre-defined timeslot (3) Adaptive
(3) The first result of the sequence is adopted as putation
the solution and worked as the basis for the next
optimization loop while time is receding
(1) Embed intelligent algorithms as a search
Intelligent control [100–109] optimization for the desired tracking result; (1) Easy to implement;
(Fuzzy logic, NN, and GA) (2) Take searching cost as the objective function; (2) Adaptive. Large computation.
(3) Optimization through iterations.
x x
R
b y y
a
A B
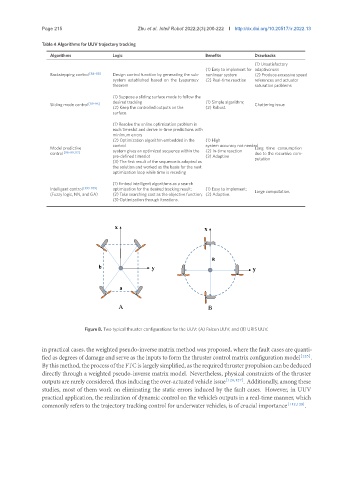
Figure 8. Two typical thruster configurations for the UUV: (A) Falcon UUV; and (B) URIS UUV.
in practical cases, the weighted pseudo-inverse matrix method was proposed, where the fault cases are quanti-
fied as degrees of damage and serve as the inputs to form the thruster control matrix configuration model [125] .
Bythis method, the processofthe FTC is largely simplified, as the required thruster propulsion canbe deduced
directly through a weighted pseudo-inverse matrix model. Nevertheless, physical constraints of the thruster
outputs are rarely considered, thus inducing the over-actuated vehicle issue [126,127] . Additionally, among these
studies, most of them work on eliminating the static errors induced by the fault cases. However, in UUV
practical application, the realization of dynamic control on the vehicle’s outputs in a real-time manner, which
commonly refers to the trajectory tracking control for underwater vehicles, is of crucial importance [112,128] .