Page 55 - Read Online
P. 55
Page 148 Ortiz et al. Intell Robot 2021;1(2):131-50 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2021.09
E EKF E EKF-DI
0.06 a a
E a 0.04
0.02
0
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400
Time [s]
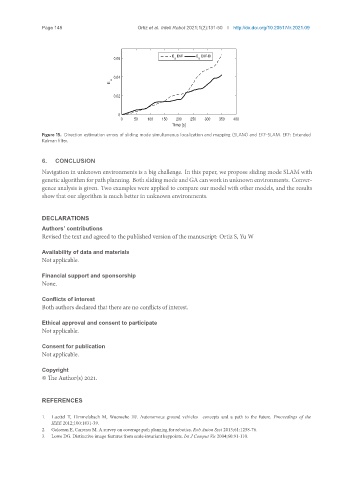
Figure 15. Direction estimation errors of sliding mode simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) and EKF-SLAM. EKF: Extended
Kalman filter.
6. CONCLUSION
Navigation in unknown environments is a big challenge. In this paper, we propose sliding mode SLAM with
genetic algorithm for path planning. Both sliding mode andGA can work in unknownenvironments. Conver-
gence analysis is given. Two examples were applied to compare our model with other models, and the results
show that our algorithm is much better in unknown environments.
DECLARATIONS
Authors’ contributions
Revised the text and agreed to the published version of the manuscript: Ortiz S, Yu W
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Financial support and sponsorship
None.
Conflicts of interest
Both authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Copyright
© The Author(s) 2021.
REFERENCES
1. Luettel T, Himmelsbach M, Wuensche HJ. Autonomous ground vehicles—concepts and a path to the future. Proceedings of the
IEEE 2012;100:183139.
2. Galceran E, Carreras M. A survey on coverage path planning for robotics. Rob Auton Syst 2013;61:125876.
3. Lowe DG. Distinctive image features from scaleinvariant keypoints. Int J Comput Vis 2004;60:91110.