Page 41 - Read Online
P. 41
Page 510 Liu et al. Intell Robot 2024;4(4):503-23 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2024.29
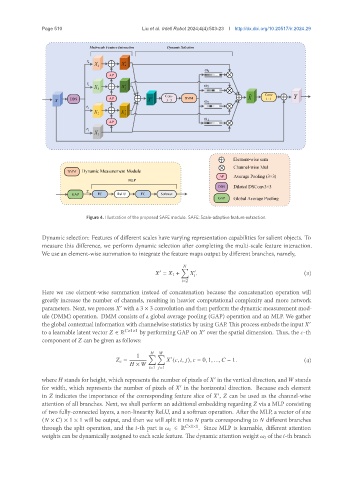
Figure 4. Illustration of the proposed SAFE module. SAFE: Scale-adaptive feature extraction.
Dynamic selection: Features of different scales have varying representation capabilities for salient objects. To
measure this difference, we perform dynamic selection after completing the multi-scale feature interaction.
We use an element-wise summation to integrate the feature maps output by different branches, namely,
Õ
′ ′ (3)
= 1 + .
=2
Here we use element-wise summation instead of concatenation because the concatenation operation will
greatly increase the number of channels, resulting in heavier computational complexity and more network
parameters. Next, we process with a 3 × 3 convolution and then perform the dynamic measurement mod-
′
ule (DMM) operation. DMM consists of a global average pooling (GAP) operation and an MLP. We gather
the global contextual information with channelwise statistics by using GAP. This process embeds the input ′
′
to a learnable latent vector ∈ R ×1×1 by performing GAP on over the spatial dimension. Thus, the -th
component of can be given as follows:
1 Õ Õ
′
= ( , , ), = 0, 1, ..., − 1. (4)
×
=1 =1
where stands for height, which represents the number of pixels of in the vertical direction, and stands
′
for width, which represents the number of pixels of in the horizontal direction. Because each element
′
in indicates the importance of the corresponding feature slice of , can be used as the channel-wise
′
attention of all branches. Next, we shall perform an additional embedding regarding via a MLP consisting
of two fully-connected layers, a non-linearity ReLU, and a softmax operation. After the MLP, a vector of size
( × ) × 1 × 1 will be output, and then we will split it into parts corresponding to different branches
through the split operation, and the -th part is ∈ R ×1×1 . Since MLP is learnable, different attention
weights can be dynamically assigned to each scale feature. The dynamic attention weight of the -th branch