Page 116 - Read Online
P. 116
Page 64 Guan et al. Intell Robot 2024;4(1):61-73 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2024.04
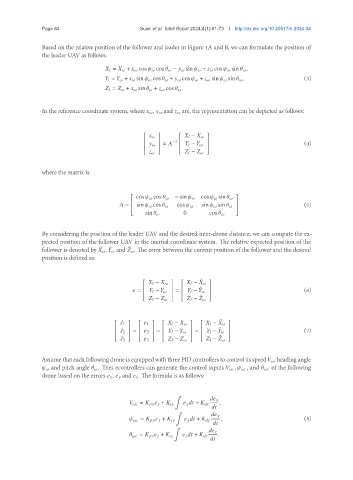
Based on the relative position of the follower and leader in Figure 1A and B, we can formulate the position of
the leader UAV as follows:
= + cos cos − sin + cos sin ,
= + sin cos + cos + sin sin , (3)
= + sin + cos .
In the reference coordinate system, where , ,and are, the representation can be depicted as follows:
−
= −1 (4)
−
−
where the matrix is:
cos cos − sin cos sin
= sin cos cos (5)
sin sin
sin 0 cos
By considering the position of the leader UAV and the desired inter-drone distance, we can compute the ex-
pected position of the follower UAV in the inertial coordinate system. The relative expected position of the
follower is denoted by , and . The error between the current position of the follower and the desired
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
position is defined as:
ˆ
− −
= = ˆ (6)
− −
ˆ
− −
ˆ
1 1 − −
= = = ˆ (7)
2 2 − −
ˆ
3 3 − −
Assume that each following drone is equipped with three PID controllers to control its speed , heading angle
and pitch angle . Thes econtrollers can generate the control inputs , , and of the following
drone based on the errors , and . The formula is as follows:
∫
= + + ,
∫
= + + , (8)
∫
= + + .