Page 855 - Read Online
P. 855
Page 6 of 16 Silk et al. Hepatoma Res 2020;6:73 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2020.61
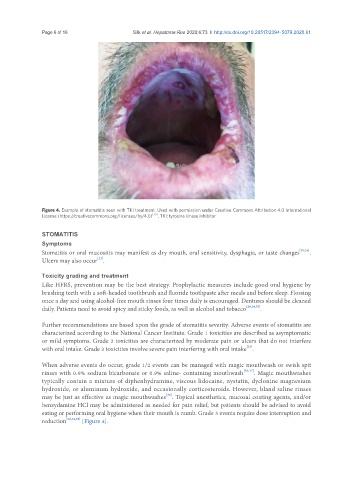
Figure 4. Example of stomatitis seen with TKI treatment. Used with permission under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International
License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0) [39] . TKI: tyrosine kinase inhibitor
STOMATITIS
Symptoms
Stomatitis or oral mucositis may manifest as dry mouth, oral sensitivity, dysphagia, or taste changes [29,34] .
[22]
Ulcers may also occur .
Toxicity grading and treatment
Like HFRS, prevention may be the best strategy. Prophylactic measures include good oral hygiene by
brushing teeth with a soft-headed toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste after meals and before sleep. Flossing
once a day and using alcohol-free mouth rinses four times daily is encouraged. Dentures should be cleaned
daily. Patients need to avoid spicy and sticky foods, as well as alcohol and tobacco [29,34,35] .
Further recommendations are based upon the grade of stomatitis severity. Adverse events of stomatitis are
characterized according to the National Cancer Institute. Grade 1 toxicities are described as asymptomatic
or mild symptoms. Grade 2 toxicities are characterized by moderate pain or ulcers that do not interfere
[23]
with oral intake. Grade 3 toxicities involve severe pain interfering with oral intake .
When adverse events do occur, grade 1/2 events can be managed with magic mouthwash or swish spit
rinses with 0.9% sodium bicarbonate or 0.9% saline- containing mouthwash [36,37] . Magic mouthwashes
typically contain a mixture of diphenhydramine, viscous lidocaine, nystatin, dyclonine magnesium
hydroxide, or aluminum hydroxide, and occasionally corticosteroids. However, bland saline rinses
[36]
may be just as effective as magic mouthwashes . Topical anesthetics, mucosal coating agents, and/or
benzydamine HCl may be administered as needed for pain relief, but patients should be advised to avoid
eating or performing oral hygiene when their mouth is numb. Grade 3 events require dose interruption and
reduction [22,34,38] [Figure 4].