Page 102 - Read Online
P. 102
Bhatia et al. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:9 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.04 Page 11 of 16
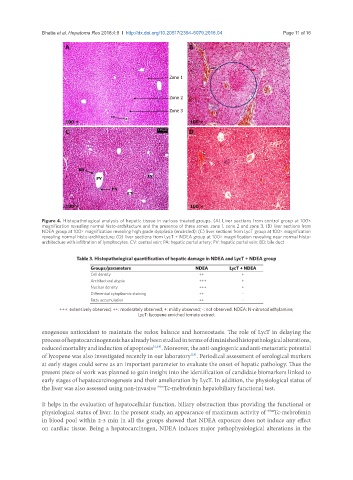
A B
Zone 1
Zone 2
Zone 3
100 × 100 ×
C D
100 × 100 ×
Figure 4. Histopathological analysis of hepatic tissue in various treated groups. (A) Liver sections from control group at 100×
magnification revealing normal histo-architecture and the presence of three zones: zone 1, zone 2 and zone 3; (B) liver sections from
NDEA group at 100× magnification revealing high grade dysplasia (encircled); (C) liver sections from LycT group at 100× magnification
revealing normal histo-architecture; (D) liver sections from LycT + NDEA group at 100× magnification revealing near normal histo-
architecture with infiltration of lymphocytes. CV: central vein; PA: hepatic portal artery; PV: hepatic portal vein; BD: bile duct
Table 3. Histopathological quantification of hepatic damage in NDEA and LycT + NDEA group
Groups/parameters NDEA LycT + NDEA
Cell density ++ +
Architectural atypia +++ +
Nuclear density +++ +
Differential cytoplasmic staining ++ -
Fatty accumulation ++ -
+++: extensively observed; ++: moderately observed; +: mildly observed; -: not observed. NDEA: N-nitrosodiethylamine;
LycT: lycopene enriched tomato extract
exogenous antioxidant to maintain the redox balance and homeostasis. The role of LycT in delaying the
process of hepatocarcinogenesis has already been studied in terms of diminished histopathological alterations,
reduced mortality and induction of apoptosis [3,18] . Moreover, the anti-angiogenic and anti-metastatic potential
of lycopene was also investigated recently in our laboratory . Periodical assessment of serological markers
[23]
at early stages could serve as an important parameter to evaluate the onset of hepatic pathology. Thus the
present piece of work was planned to gain insight into the identification of candidate biomarkers linked to
early stages of hepatocarcinogenesis and their amelioration by LycT. In addition, the physiological status of
99m
the liver was also assessed using non-invasive Tc-mebrofenin hepatobiliary functional test.
It helps in the evaluation of hepatocellular function, biliary obstruction thus providing the functional or
physiological status of liver. In the present study, an appearance of maximum activity of Tc-mebrofenin
99m
in blood pool within 2-3 min in all the groups showed that NDEA exposure does not induce any effect
on cardiac tissue. Being a hepatocarcinogen, NDEA induces major pathophysiological alterations in the