Page 132 - Read Online
P. 132
El-Gazzar et al. Gadobenate dimeglumine dynamic MRI for early HCC detection
metabolism is mostly unaltered are expected to
Arterial
supply uptake multihance and excrete the compound into
Portal venous supply the bile. Such lesions are typically benign and usually
Hepatic arterial supply
Abnormal arterial supply appear isointense or hyperintense as compared to
the normal liver parenchyma in the hepatobiliary
phase of MRI. In contrast, lesions lacking functioning
hepatocytes where hepatobiliary metabolism is
blocked or inhibited are generally not able to uptake
and excrete multihance into the bile. Such lesions are
typically malignant and usually appear hypointense
as compared to the normal liver parenchyma on the
Portal supply hepatobiliary phase of MRI. [10,11] Therefore, multihance
RN Low DN High DN Early HCC Well HCC Moderately dynamic MRI is a potential promising diagnostic
HCC modality for detection of early HCC.
[4]
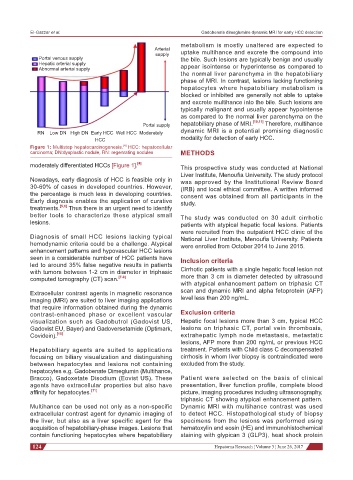
Figure 1: Multistep hepatocarcinogenesis. HCC: hepatocellular
carcinoma; DN:dysplastic nodule, RN: regenrating nodules METHODS
moderately differentiated HCCs [Figure 1]. [4] This prospective study was conducted at National
Liver Institute, Menoufia University. The study protocol
Nowadays, early diagnosis of HCC is feasible only in was approved by the Institutional Review Board
30-60% of cases in developed countries. However, (IRB) and local ethical committee. A written informed
the percentage is much less in developing countries. consent was obtained from all participants in the
Early diagnosis enables the application of curative study.
treatments. [5,6] Thus there is an urgent need to identify
better tools to characterize these atypical small The study was conducted on 30 adult cirrhotic
lesions. patients with atypical hepatic focal lesions. Patients
were recruited from the outpatient HCC clinic of the
Diagnosis of small HCC lesions lacking typical National Liver Institute, Menoufia University. Patients
hemodynamic criteria could be a challenge. Atypical were enrolled from October 2014 to June 2015.
enhancement patterns and hypovascular HCC lesions
seen in a considerable number of HCC patients have Inclusion criteria
led to around 35% false negative results in patients
with tumors between 1-2 cm in diameter in triphasic Cirrhotic patients with a single hepatic focal lesion not
computed tomography (CT) scan. [7-9] more than 3 cm in diameter detected by ultrasound
with atypical enhancement pattern on triphasic CT
Extracellular contrast agents in magnetic resonance scan and dynamic MRI and alpha fetoprotein (AFP)
imaging (MRI) are suited to liver imaging applications level less than 200 ng/mL.
that require information obtained during the dynamic
contrast-enhanced phase or excellent vascular Exclusion criteria
visualization such as Gadobutrol (Gadovist US, Hepatic focal lesions more than 3 cm, typical HCC
Gadovist EU, Bayer) and Gadoversetamide (Optimark, lesions on triphasic CT, portal vein thrombosis,
Covidein). [10] extrahepatic lymph node metastasis, metastatic
lesions, AFP more than 200 ng/mL or previous HCC
Hepatobiliary agents are suited to applications treatment. Patients with Child class C decompensated
focusing on biliary visualization and distinguishing cirrhosis in whom liver biopsy is contraindicated were
between hepatocytes and lesions not containing excluded from the study.
hepatocytes e.g. Gadobenate Dimeglumin (Multihance,
Bracco), Gadoxetate Disodium (Eovist US). These Patient were selected on the basis of clinical
agents have extracellular properties but also have presentation, liver function profile, complete blood
affinity for hepatocytes. [11] picture, imaging procedures including ultrasonography,
triphasic CT showing atypical enhancement pattern.
Multihance can be used not only as a non-specific Dynamic MRI with multihance contrast was used
extracellular contrast agent for dynamic imaging of to detect HCC. Histopathological study of biopsy
the liver, but also as a liver specific agent for the specimens from the lesions was performed using
acquisition of hepatobiliary-phase images. Lesions that hematoxylin and eosin (HE) and immunohistochemical
contain functioning hepatocytes where hepatobiliary staining with glypican 3 (GLP3), heat shock protein
124 Hepatoma Research ¦ Volume 3 ¦ June 26, 2017