Page 99 - Read Online
P. 99
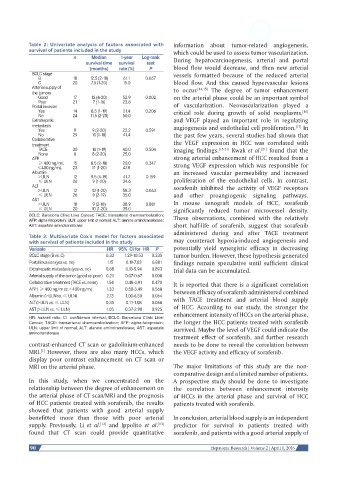
Table 2: Univariate analysis of factors associated with information about tumor-related angiogenesis,
survival of patients included in the study which could be used to assess tumor vascularization.
n Median 1-year Log-rank During hepatocarcinogenesis, arterial and portal
survival time survival test
(months) rate (%) P blood flow would decrease, and then new arterial
BCLC stage vessels formatted because of the reduced arterial
B 18 12.5 (2-18) 61.1 0.067
C 20 7.5 (1-20) 15.0 blood flow. And this caused hypervascular lesions
Arterial supply of to occur. [14,15] The degree of tumor enhancement
the tumors
Good 17 12 (4-20) 52.9 0.002 on the arterial phase could be an important symbol
Poor 21 7 (1-16) 23.8
Portal invasion of vascularization. Neovascularization played a
Yes 14 8.5 (1-19) 21.4 0.206 critical role during growth of solid neoplasms,
[16]
No 24 11.5 (2-20) 50.0
Extrahepatic and VEGF played an important role in regulating
metastasis angiogenesis and endothelial cell proliferation. In
[17]
Yes 9 9 (2-20) 22.2 0.591
No 29 10 (1-18) 41.4 the past few years, several studies had shown that
Collaborative
treatment the VEGF expression in HCC was correlated with
TACE 30 10 (1-19) 40.0 0.504 imaging findings. [18-21] Kwak et al. found that the
[21]
None 8 8 (2-20) 25.0
AFP strong arterial enhancement of HCC resulted from a
≥ 400 ng/mL 15 8.5 (2-18) 20.0 0.347 strong VEGF expression which was responsible for
< 400 ng/mL 23 11 (1-20) 47.8
Albumin an increased vascular permeability and increased
> ULN 12 9.5 (4-19) 41.7 0.159
≤ ULN 26 9 (1-20) 34.6 proliferation of the endothelial cells. In contrast,
ALT sorafenib inhibited the activity of VEGF receptors
> ULN 12 13 (1-20) 58.3 0.063
≤ ULN 26 9 (2-19) 35.0 and other proangiogenic signaling pathways.
AST
> ULN 18 9 (2-18) 38.9 0.881 In mouse xenograft models of HCC, sorafenib
≤ ULN 20 10 (1-20) 35.0 significantly reduced tumor microvessel density.
BCLC: Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer; TACE: transarterial chemoembolization; These observations, combined with the relatively
AFP: alpha-fetoprotein; ULN: upper limit of normal; ALT: alanine aminotransferase;
AST: aspartate aminotransferase short half-life of sorafenib, suggest that sorafenib
administered during and after TACE treatment
Table 3: Multivariate Cox’s model for factors associated
with survival of patients included in the study may counteract hypoxia-induced angiogenesis and
Variable HR 95% CI for HR P potentially yield synergistic efficacy in decreasing
BCLC stage (B vs. C) 0.33 1.29-10.53 0.335 tumor burden. However, these hypothesis generated
Portal invasion (yes vs. no) 1.15 0.19-7.03 0.881 findings remain speculative until sufficient clinical
Extrahepatic metastasis (yes vs. no) 0.88 0.13-5.94 0.893 trial data can be accumulated.
Arterial supply of the tumor (good vs. poor) 0.21 0.07-0.67 0.008
Collaborative treatment (TACE vs. none) 1.54 0.48-4.91 0.470 It is reported that there is a significant correlation
AFP ( ≥ 400 ng/m vs. < 400 ng/m) 1.33 0.50-3.49 0.568 between efficacy of sorafenib administered combined
Albumin (> ULN vs. ≤ ULN) 2.13 1.00-6.50 0.064 with TACE treatment and arterial blood supply
ALT (> ULN vs. ≤ ULN) 0.35 0.11-1.08 0.068
AST (> ULN vs. ≤ ULN) 1.05 0.37-2.98 0.925 of HCC. According to our study, the stronger the
enhancement intensity of HCCs on the arterial phase,
HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval; BCLC: Barcelona Clinic Liver
Cancer; TACE: transarterial chemoembolization; AFP: alpha-fetoprotein; the longer the HCC patients treated with sorafenib
ULN: upper limit of normal; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; AST: aspartate survived. Maybe the level of VEGF could indicate the
aminotransferase
treatment effect of sorafenib, and further research
contrast-enhanced CT scan or gadolinium-enhanced needs to be done to reveal the correlation between
MRI. However, there are also many HCCs, which the VEGF activity and efficacy of sorafenib.
[1]
display poor contrast enhancement on CT scan or
MRI on the arterial phase. The major limitations of this study are the non-
comparative design and a limited number of patients.
In this study, when we concentrated on the A prospective study should be done to investigate
relationship between the degree of enhancement on the correlation between enhancement intensity
the arterial phase of CT scan/MRI and the prognosis of HCCs in the arterial phase and survival of HCC
of HCC patients treated with sorafenib, the results patients treated with sorafenib.
showed that patients with good arterial supply
benefitted more than those with poor arterial In conclusion, arterial blood supply is an independent
[13]
[12]
supply. Previously, Li et al. and Ippolito et al. predictor for survival in patients treated with
found that CT scan could provide quantitative sorafenib, and patients with a good arterial supply of
90 Hepatoma Research | Volume 2 | April 1, 2016