Page 102 - Read Online
P. 102
complete physical examination, laboratory investigations
[complete blood count, coagulation profile, liver function
test, kidney function test and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)], and
radiological investigations [abdominal ultrasonography
and triphasic computerized tomography (CT)]. They
were categorized into two groups. Group A: 20 patients
for whom HR was done (according to the size, site and
number of tumors); Group B: 20 patients for whom RFA
was done using percutaneous ultrasonography.
Inclusion criteria
Patients with or without liver cirrhosis. Patients with
Child A and B (Child-Pugh classification). Patients with
or without hepatitis B or C infection. Patients who have
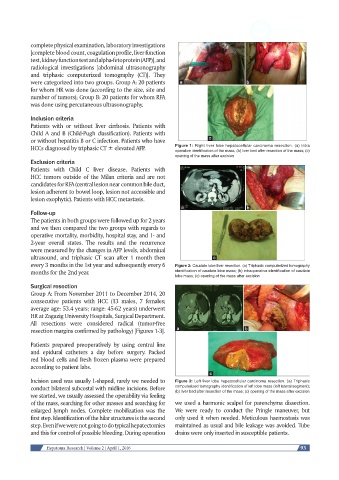
HCCs diagnosed by triphasic CT ± elevated AFP. Figure 1: Right liver lobe hepatocellular carcinoma resection. (a) Intra
operative identification of the mass; (b) liver bed after resection of the mass; (c)
opening of the mass after excision
Exclusion criteria
Patients with Child C liver disease. Patients with
HCC tumors outside of the Milan criteria and are not
candidates for RFA (central lesion near common bile duct,
lesion adherent to bowel loop, lesion not accessible and
lesion exophytic). Patients with HCC metastasis.
Follow-up
The patients in both groups were followed up for 2 years
and we then compared the two groups with regards to
operative mortality, morbidity, hospital stay, and 1- and
2-year overall states. The results and the recurrence
were measured by the changes in AFP levels, abdominal
ultrasound, and triphasic CT scan after 1 month then
every 3 months in the 1st year and subsequently every 6 Figure 2: Caudate lobe liver resection. (a) Triphasic computerized tomography
months for the 2nd year. identification of caudate lobe mass; (b) intraoperative identification of caudate
lobe mass; (c) opening of the mass after excision
Surgical resection
Group A: From November 2011 to December 2014, 20
consecutive patients with HCC (13 males, 7 females;
average age: 53.4 years; range: 45-62 years) underwent
HR at Zagazig University Hospitals, Surgical Department.
All resections were considered radical (tumor-free
resection margins confirmed by pathology) [Figures 1-3].
Patients prepared preoperatively by using central line
and epidural catheters a day before surgery. Packed
red blood cells and fresh frozen plasma were prepared
according to patient labs.
Incision used was usually L-shaped, rarely we needed to Figure 3: Left liver lobe hepatocellular carcinoma resection. (a) Triphasic
conduct bilateral subcostal with midline incisions. Before computerized tomography identification of left lobe mass (left lateral segment);
(b) liver bed after resection of the mass; (c) opening of the mass after excision
we started, we usually assessed the operability via feeling
of the mass, searching for other masses and searching for we used a harmonic scalpel for parenchyma dissection.
enlarged lymph nodes. Complete mobilization was the We were ready to conduct the Pringle maneuver, but
first step. Identification of the hilar structures is the second only used it when needed. Meticulous haemostasis was
step. Even if we were not going to do typical hepatectomies maintained as usual and bile leakage was avoided. Tube
and this for control of possible bleeding. During operation drains were only inserted in susceptible patients.
Hepatoma Research | Volume 2 | April 1, 2016 93