Page 334 - Read Online
P. 334
Lee et al. Liver resection in obese
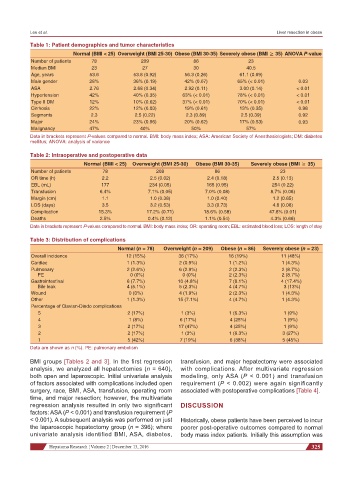
Table 1: Patient demographics and tumor characteristics
Normal (BMI < 25) Overweight (BMI 25-30) Obese (BMI 30-35) Severely obese (BMI ≥ 35) ANOVA P-value
Number of patients 78 209 86 23
Median BMI 23 27 30 40.5
Age, years 53.6 53.8 (0.92) 56.3 (0.26) 61.1 (0.69)
Male gender 28% 36% (0.19) 42% (0.07) 65% (< 0.01) 0.03
ASA 2.76 2.68 (0.34) 2.92 (0.11) 3.00 (0.14) < 0.01
Hypertension 42% 40% (0.35) 63% (< 0.01) 78% (< 0.01) < 0.01
Type II DM 12% 10% (0.62) 37% (< 0.01) 70% (< 0.01) < 0.01
Cirrhosis 22% 12% (0.03) 19% (0.61) 13% (0.35) 0.98
Segments 2.3 2.5 (0.22) 2.3 (0.89) 2.5 (0.39) 0.92
Major 24% 23% (0.96) 20% (0.62) 17% (0.53) 0.93
Malignancy 47% 40% 50% 57%
Data in brackets represent P-values compared to normal. BMI: body mass index; ASA: American Society of Anesthesiologists; DM: diabetes
mellitus; ANOVA: analysis of variance
Table 2: Intraoperative and postoperative data
Normal (BMI < 25) Overweight (BMI 25-30) Obese (BMI 30-35) Severely obese (BMI ≥ 35)
Number of patients 78 209 86 23
OR time (h) 2.2 2.5 (0.02) 2.4 (0.18) 2.5 (0.13)
EBL (mL) 177 234 (0.05) 165 (0.95) 254 (0.22)
Transfusion 6.4% 7.1% (0.05) 7.0% (0.08) 8.7% (0.08)
Margin (cm) 1.1 1.0 (0.38) 1.0 (0.40) 1.2 (0.65)
LOS (days) 3.5 3.2 (0.53) 3.3 (0.73) 4.6 (0.08)
Complication 15.3% 17.2% (0.71) 18.6% (0.58) 47.8% (0.01)
Deaths 2.5% 0.4% (0.12) 1.1% (0.54) 4.3% (0.66)
Data in brackets represent P-values compared to normal. BMI: body mass index; OR: operating room; EBL: estimated blood loss; LOS: length of stay
Table 3: Distribution of complications
Normal (n = 78) Overweight (n = 209) Obese (n = 86) Severely obese (n = 23)
Overall incidence 12 (15%) 36 (17%) 16 (19%) 11 (48%)
Cardiac 1 (1.3%) 2 (0.9%) 1 (1.2%) 1 (4.3%)
Pulmonary 2 (2.6%) 6 (2.9%) 2 (2.3%) 2 (8.7%)
PE 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 2 (2.3%) 2 (8.7%)
Gastrointestinal 6 (7.7%) 10 (4.8%) 7 (8.1%) 4 (17.4%)
Bile leak 4 (5.1%) 5 (2.3%) 4 (4.7%) 3 (13%)
Wound 0 (0%) 4 (1.9%) 2 (2.3%) 1 (4.3%)
Other 1 (1.3%) 15 (7.1%) 4 (4.7%) 1 (4.3%)
Percentage of Clavian-Dindo complications
5 2 (17%) 1 (3%) 1 (6.3%) 1 (9%)
4 1 (8%) 6 (17%) 4 (25%) 1 (9%)
3 2 (17%) 17 (47%) 4 (25%) 1 (9%)
2 2 (17%) 1 (3%) 1 (6.3%) 3 (27%)
1 5 (42%) 7 (19%) 6 (38%) 5 (45%)
Data are shown as n (%). PE: pulmonary embolism
BMI groups [Tables 2 and 3]. In the first regression transfusion, and major hepatectomy were associated
analysis, we analyzed all hepatectomies (n = 640), with complications. After multivariate regression
both open and laparoscopic. Initial univariate analysis modeling, only ASA (P < 0.001) and transfusion
of factors associated with complications included open requirement (P < 0.002) were again significantly
surgery, race, BMI, ASA, transfusion, operating room associated with postoperative complications [Table 4].
time, and major resection; however, the multivariate
regression analysis resulted in only two significant DISCUSSION
factors: ASA (P < 0.001) and transfusion requirement (P
< 0.001). A subsequent analysis was performed on just Historically, obese patients have been perceived to incur
the laparoscopic hepatectomy group (n = 396); where poorer post-operative outcomes compared to normal
univariate analysis identified BMI, ASA, diabetes, body mass index patients. Initially this assumption was
Hepatoma Research ¦ Volume 2 ¦ December 13, 2016 325