Page 97 - Read Online
P. 97
complete tumor response. The complications associated
with perRFA reported in the literature include intraperitoneal
hemorrhage, hepatic infarction, hepatic abscess formation,
intestinal perforation, bile peritonitis, and carcinoma seeding.
Laparoscopic RFA of HCC is associated with a low rate of major
complications, most of them related to bleeding from hepatic
puncture sites or trocar accesses and to iatrogenic malignant
seeding. We reported only one case of major bleeding
requiring reintervention, and no tumor spread was observed.
There were no treatment-related deaths in our series.
In the literature, few reviews of minimally invasive RFA
are available, since most surgical RFA procedures are still
performed by laparotomy. Today the advantages that the
[6]
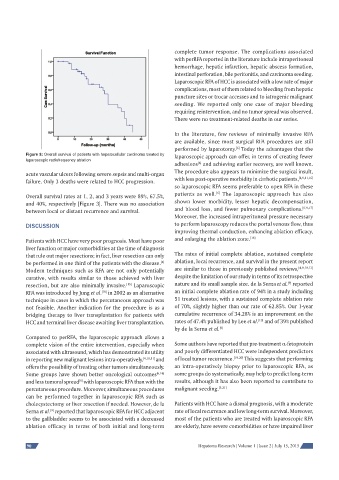
Figure 3: Overall survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by laparoscopic approach can offer, in terms of creating fewer
laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation
adhesions and achieving earlier recovery, are well known.
[4]
acute vascular ulcers following severe sepsis and multi-organ The procedure also appears to minimize the surgical insult,
failure. Only 3 deaths were related to HCC progression. with less post-operative morbidity in cirrhotic patients, [4,9,11,16]
so laparoscopic RFA seems preferable to open RFA in these
[6]
Overall survival rates at 1, 2, and 3 years were 89%, 67.5%, patients as well. The laparoscopic approach has also
and 40%, respectively [Figure 3]. There was no association shown lower morbidity, lesser hepatic decompensation,
between local or distant recurrence and survival. and blood loss, and fewer pulmonary complications. [6,9,17]
Moreover, the increased intraperitoneal pressure necessary
DISCUSSION to perform laparoscopy reduces the portal venous flow, thus
improving thermal conduction, enhancing ablation efficacy,
Patients with HCC have very poor prognosis. Most have poor and enlarging the ablation zone. [18]
liver function or major comorbidities at the time of diagnosis
that rule out major resections; in fact, liver resection can only The rates of initial complete ablation, sustained complete
be performed in one third of the patients with the disease. ablation, local recurrence, and survival in the present report
[4]
Modern techniques such as RFA are not only potentially are similar to those in previously published reviews, [4,9,10,13]
curative, with results similar to those achieved with liver despite the limitation of our study in terms of its retrospective
[9]
resection, but are also minimally invasive. Laparoscopic nature and its small sample size. de la Serna et al. reported
[15]
RFA was introduced by Jung et al. in 2002 as an alternative an initial complete ablation rate of 94% in a study including
[16]
technique in cases in which the percutaneous approach was 51 treated lesions, with a sustained complete ablation rate
not feasible. Another indication for the procedure is as a of 70%, slightly higher than our rate of 62.85%. Our 1-year
bridging therapy to liver transplantation for patients with cumulative recurrence of 34.28% is an improvement on the
[10]
HCC and terminal liver disease awaiting liver transplantation. rates of 47.4% published by Lee et al. and of 39% published
by de la Serna et al. [9]
Compared to perRFA, the laparoscopic approach allows a
complete vision of the entire intervention, especially when Some authors have reported that pre-treatment α-fetoprotein
associated with ultrasound, which has demonstrated its utility and poorly differentiated HCC were independent predictors
in reporting new malignant lesions intra-operatively, [4,10,11] and of local tumor recurrence. [19,20] This suggests that performing
offers the possibility of treating other tumors simultaneously. an intra-operatively biopsy prior to laparoscopic RFA, as
Some groups have shown better oncological outcomes [6,16] some groups do systematically, may help to predict long-term
and less tumoral spread with laparoscopic RFA than with the results, although it has also been reported to contribute to
[9]
percutaneous procedure. Moreover, simultaneous procedures malignant seeding. [5,21]
can be performed together in laparoscopic RFA such as
cholecystectomy or liver resection if needed. However, de la Patients with HCC have a dismal prognosis, with a moderate
Serna et al. reported that laparoscopic RFA for HCC adjacent rate of local recurrence and low long-term survival. Moreover,
[9]
to the gallbladder seems to be associated with a decreased most of the patients who are treated with laparoscopic RFA
ablation efficacy in terms of both initial and long-term are elderly, have severe comorbidities or have impaired liver
90 Hepatoma Research | Volume 1 | Issue 2 | July 15, 2015