Page 34 - Read Online
P. 34
Table 2: The recurrence of all studied patients as regard
all risk factors after RFA Survival of the three groups
100
Group Recurrence of HCC as Recurrent
regard independent lesions
risk factors
Risk factor n n (%) P
I (n = 37) AFP 200 13 4 (30.7) 0.0423
AFP < 200 24 1 (4)
Solitary nodule 24 1 (4) 0.0423 Survival% 50
Multiple nodules 13 4 (30.7) Group I
Nodule diameter 3 cm 11 4 (36.3) 0.0207 Group II
Nodule diameter < 3 cm 26 1 (3.8)
Group III
BMI 25 23 3 (13) 1.0000
BMI < 25 14 2 (14)
Cumulative 37 5 (13) 0
II (n = 25) AFP 200 11 10 (90.9) 0.0421 0 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 33 36
AFP < 200 14 7 (50) Months
Solitary nodule 9 3 (33.3) 0.0099
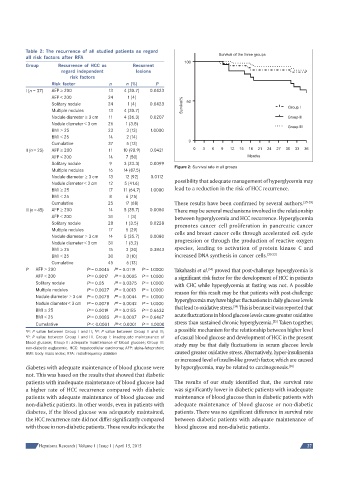
Figure 2: Survival rate in all groups
Multiple nodules 16 14 (87.5)
Nodule diameter 3 cm 13 12 (92) 0.0112
Nodule diameter < 3 cm 12 5 (41.6) possibility that adequate management of hyperglycemia may
BMI 25 17 11 (64.7) 1.0000 lead to a reduction in the risk of HCC recurrence.
BMI < 25 8 6 (75)
Cumulative 25 17 (68) These results have been confirmed by several authors. [25-29]
III (n = 45) AFP 200 14 5 (35.7) 0.0080 There may be several mechanisms involved in the relationship
AFP < 200 31 1 (3) between hyperglycemia and HCC recurrence. Hyperglycemia
Solitary nodule 28 1 (3.5) 0.0228
promotes cancer cell proliferation in pancreatic cancer
Multiple nodules 17 5 (29)
cells and breast cancer cells through accelerated cell cycle
Nodule diameter 3 cm 14 5 (35.7) 0.0080
progression or through the production of reactive oxygen
Nodule diameter < 3 cm 31 1 (3.2)
species, leading to activation of protein kinase C and
BMI 25 15 3 (20) 0.3843
BMI < 25 30 3 (10) increased DNA synthesis in cancer cells. [30-33]
Cumulative 45 6 (13)
c
a
b
[34]
P AFP 200 P = 0.0045 P = 0.0119 P = 1.0000 Takahashi et al. proved that post-challenge hyperglycemia is
a
AFP < 200 P = 0.0017 P = 0.0005 P = 1.0000 a significant risk factor for the development of HCC in patients
c
b
Solitary nodule P = 0.05 P = 0.0375 P = 1.0000 with CHC while hyperglycemia at fasting was not. A possible
a
c
b
Multiple nodules P = 0.0027 P = 0.0013 P = 1.0000 reason for this result may be that patients with post-challenge
a
b
c
c
b
a
Nodule diameter 3 cm P = 0.0078 P = 0.0044 P = 1.0000 hyperglycemia may have higher fluctuations in daily glucose levels
c
b
a
Nodule diameter < 3 cm P = 0.0078 P = 0.0042 P = 1.0000 that lead to oxidative stress. This is because it was reported that
[34]
b
BMI 25 P = 0.0019 P = 0.0155 P = 0.6632
a
c
b
c
BMI < 25 P = 0.0083 P = 0.0007 P = 0.6467 acute fluctuations in blood glucose levels cause greater oxidative
a
[35]
stress than sustained chronic hyperglycemia. Taken together,
c
a
Cumulative P < 0.0001 P < 0.0001 P = 1.0000
b
a possible mechanism for the relationship between higher level
a b
P: P value between Group I and II; P: P value between Group II and III;
c P: P value between Group I and III. Group I: inadequate maintenance of of casual blood glucose and development of HCC in the present
blood glucose; Group II: adequate maintenance of blood glucose; Group III: study may be that daily fluctuations in serum glucose levels
non-diabetic euglycemic. HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; AFP: alpha-fetoprotein;
BMI: body mass index; RFA: radiofrequency ablation caused greater oxidative stress. Alternatively, hyper-insulinemia
or increased level of insulin-like growth factor, which are caused
diabetes with adequate maintenance of blood glucose were by hyperglycemia, may be related to carcinogenesis. [36]
not. This was based on the results that showed that diabetic
patients with inadequate maintenance of blood glucose had The results of our study identified that, the survival rate
a higher rate of HCC recurrence compared with diabetic was significantly lower in diabetic patients with inadequate
patients with adequate maintenance of blood glucose and maintenance of blood glucose than in diabetic patients with
non-diabetic patients. In other words, even in patients with adequate maintenance of blood glucose or non-diabetic
diabetes, if the blood glucose was adequately maintained, patients. There was no significant difference in survival rate
the HCC recurrence rate did not differ significantly compared between diabetic patients with adequate maintenance of
with those in non-diabetic patients. These results indicate the blood glucose and non-diabetic patients.
Hepatoma Research | Volume 1 | Issue 1 | April 15, 2015 27