Page 33 - Read Online
P. 33
lesions detected by ultrasonography showing vascular maintenance of blood glucose group and the non-diabetes
enhancement with washout on triphasic CT or dynamic group (P = 1.0000).
MRI. If the tumor was not hypervascular, a tumor biopsy was
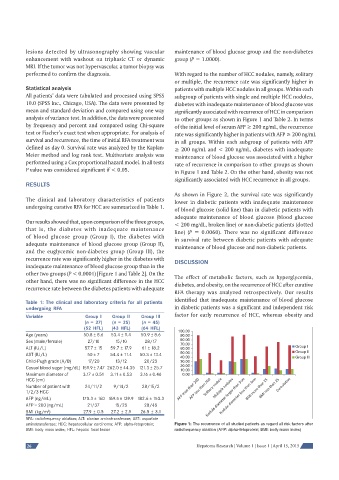
performed to confirm the diagnosis. With regard to the number of HCC nodules, namely, solitary
or multiple, the recurrence rate was significantly higher in
Statistical analysis patients with multiple HCC nodules in all groups. Within each
All patients’ data were tabulated and processed using SPSS subgroup of patients with single and multiple HCC nodules,
10.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, USA). The data were presented by diabetes with inadequate maintenance of blood glucose was
mean and standard deviation and compared using one way significantly associated with recurrence of HCC in comparison
analysis of variance test. In addition, the data were presented to other groups as shown in Figure 1 and Table 2. In terms
by frequency and percent and compared using Chi-square of the initial level of serum AFP ≥ 200 ng/mL, the recurrence
test or Fischer’s exact test when appropriate. For analysis of rate was significantly higher in patients with AFP ≥ 200 ng/mL
survival and recurrence, the time of initial RFA treatment was in all groups. Within each subgroup of patients with AFP
defined as day 0. Survival rate was analyzed by the Kaplan- ≥ 200 ng/mL and < 200 ng/mL, diabetes with inadequate
Meier method and log rank test. Multivariate analysis was maintenance of blood glucose was associated with a higher
performed using a Cox proportional hazard model. In all tests rate of recurrence in comparison to other groups as shown
P value was considered significant if < 0.05. in Figure 1 and Table 2. On the other hand, obesity was not
significantly associated with HCC recurrence in all groups.
RESULTS
As shown in Figure 2, the survival rate was significantly
The clinical and laboratory characteristics of patients lower in diabetic patients with inadequate maintenance
undergoing curative RFA for HCC are summarized in Table 1. of blood glucose (solid line) than in diabetic patients with
adequate maintenance of blood glucose (blood glucose
Our results showed that, upon comparison of the three groups, < 200 mg/dL, broken line) or non-diabetic patients (dotted
that is, the diabetes with inadequate maintenance line) (P = 0.0060). There was no significant difference
of blood glucose group (Group I), the diabetes with in survival rate between diabetic patients with adequate
adequate maintenance of blood glucose group (Group II), maintenance of blood glucose and non-diabetic patients.
and the euglycemic non-diabetes group (Group III), the
recurrence rate was significantly higher in the diabetes with DISCUSSION
inadequate maintenance of blood glucose group than in the
other two groups (P < 0.0001) [Figure 1 and Table 2]. On the The effect of metabolic factors, such as hyperglycemia,
other hand, there was no significant difference in the HCC
recurrence rate between the diabetes patients with adequate diabetes, and obesity, on the recurrence of HCC after curative
RFA therapy was analyzed retrospectively. Our results
identified that inadequate maintenance of blood glucose
Table 1: The clinical and laboratory criteria for all patients
undergoing RFA in diabetic patients was a significant and independent risk
factor for early recurrence of HCC, whereas obesity and
Variable Group I Group II Group III
(n = 37) (n = 25) (n = 45)
(52 HFL) (43 HFL) (64 HFL)
100.00
Age (years) 50.8 ± 8.6 53.4 ± 9.4 50.9 ± 8.6
90.00
Sex (male/female) 27/10 15/10 28/17 80.00
70.00
ALT (IU/L) 57.7 ± 15 59.7 ± 17.9 61 ± 18.2 60.00 Group I
AST (IU/L) 50 ± 7 54.4 ± 11.4 50.3 ± 13.4 50.00 Group II
40.00 Group III
Child-Pugh grade (A/B) 17/20 13/12 20/25 30.00
Casual blood sugar (mg/dL) 159.9 ± 7.47 262.0 ± 44.35 121.3 ± 25.7 20.00
10.00
Maximum diameter of 3.17 ± 0.51 3.11 ± 0.53 3.16 ± 0.46 0.00
HCC (cm)
Number of patient with 24/11/2 9/14/2 28/15/2
1/2/3 HCC
AFP (ng/mL) 170.3 ± 160 169.5 ± 139.9 182.6 ± 153.3
AFP 200 (ng/mL) 21/37 15/25 28/45
BMI (kg/m ) 27.9 ± 0.5 27.2 ± 2.9 26.5 ± 3.1
2
RFA: radiofrequency ablation; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; AST: aspartate
aminotransferase; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; AFP: alpha-fetoprotein; Figure 1: The recurrence of all studied patients as regard all risk factors after
BMI: body mass index; HFL: hepatic focal lesion radiofrequency ablation (AFP: alpha-fetoprotein; BMI: body mass index)
26 Hepatoma Research | Volume 1 | Issue 1 | April 15, 2015