Page 118 - Read Online
P. 118
Muñoz-Martínez et al. Hepatoma Res 2022;8:30 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2022.22 Page 7 of 11
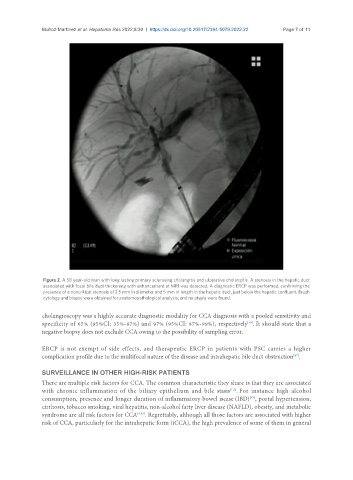
Figure 2. A 58 year-old man with long lasting primary sclerosing cholangitis and ulcerative cholangitis. A stenosis in the hepatic duct
associated with focal bile duct thickening with enhancement at MRI was detected. A diagnostic ERCP was performed, confirming the
presence of a noncritical stenosis of 2.5 mm in diameter and 5 mm in length in the hepatic duct, just below the hepatic confluent. Brush
cytology and biopsy were obtained for anatomopathological analysis, and no atypia were found.
cholangioscopy was a highly accurate diagnostic modality for CCA diagnosis with a pooled sensitivity and
specificity of 65% (95%CI: 35%-87%) and 97% (95%CI: 87%-99%), respectively . It should state that a
[46]
negative biopsy does not exclude CCA owing to the possibility of sampling error.
ERCP is not exempt of side effects, and therapeutic ERCP in patients with PSC carries a higher
[47]
complication profile due to the multifocal nature of the disease and intrahepatic bile duct obstruction .
SURVEILLANCE IN OTHER HIGH-RISK PATIENTS
There are multiple risk factors for CCA. The common characteristic they share is that they are associated
with chronic inflammation of the biliary epithelium and bile stasis . For instance high alcohol
[1,2]
[48]
consumption, presence and longer duration of inflammatory bowel isease (IBD) , portal hypertension,
cirrhosis, tobacco smoking, viral hepatitis, non-alcohol fatty liver disease (NAFLD), obesity, and metabolic
syndrome are all risk factors for CCA [4,49] . Regrettably, although all those factors are associated with higher
risk of CCA, particularly for the intrahepatic form (iCCA), the high prevalence of some of them in general